How will you effect the separation of:
(i) Two immiscible liquids
(ii) Two miscible liquids
(iii) Two organic solids differing in solubility in same solvent ?
(i) By extraction with a separating funnel.
(ii) By fractional distillation.
(iii) By fractional crystallisation.
It is based on the difference in the solubilities of the compound and impurities in a suitable solvent.
What is sublimation?
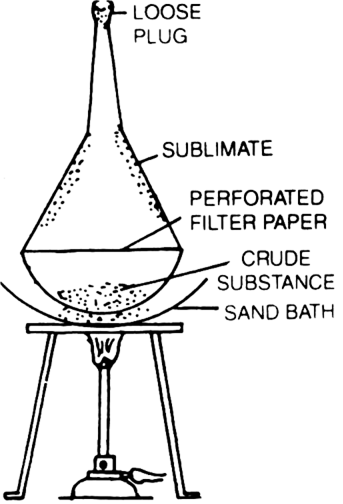
The process of repeating crystallisation for the separation of two or more solid substances (which are soluble in the same solvent but to a different extent) or cooling the hot saturated solution containing these is called fractional crystallisation. This technique is applied:
(i) to purify a solid compound containing solid impurities having different solubilities in the same solvent.
List various methods used for the purification of organic solids.
(i) Crystallisation (ii) Fractional cyrstallistaion (iii) Sublimation (iv) Differential extraction (v) Chromatography
Extraction with solvent (differential extraction): The method is based on the fact that organic substances are more soluble in organic solvents than in water. The organic substance is extracted from its aqueous solution adopting the following procedure:
1. The aqueous solution containing organic substance is shaken with a suitable organic solvent which dissolves the substance but is immiscible with water. Two layers are formed—organic layer and an aqueous layer.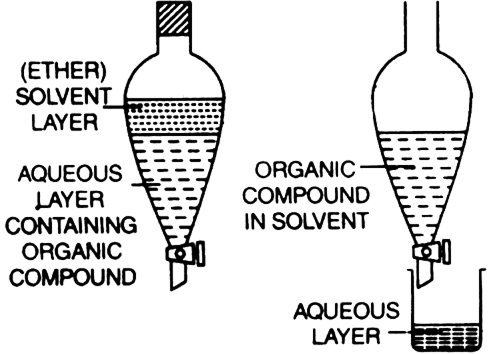
2. The solvent layer containing the organic substance (organic layer) is separated using a separating funnel. The impurities remain in the aqueous layer.
3. The organic solvent is removed by distillation to obtain the organic substance.
