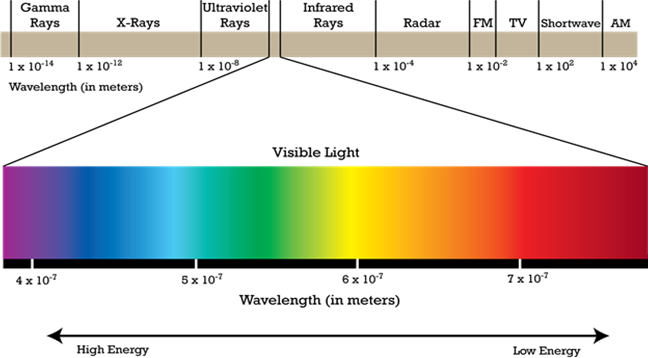
Hydrogen spectrum is an important example of line spectrum. The spectrum of hydrogen can be obtained by passing an electric discharge through the hydrogen gas taken in the discharge tube under low pressure. The radiation thus obtained is analysed with the help of a spectroscope The spectrum thus obtained contains a large number of lines present in the ultraviolet, visible and infra-red regions. These lines have been grouped into five series, each named after the name of the discoverer.
These are:
(i) Lyman series..........Ultraviolet region
(ii) Balmer series..........Visible region
(iii) Paschen series
(iv) Brackett series.........Infrared series
Though hydrogen atom contains only one electron but so many lines are obtained in the spectrum.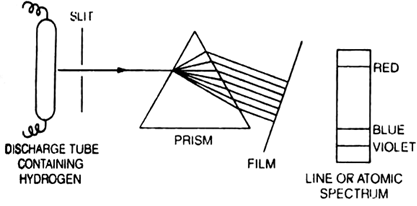
It is because of different possibilities of its excitation in its different energy levels. The lines in the visible region can be directly seen on the photographic film while the position of lines in the ultraviolet and infrared regions are located employing different techniques.
Describe briefly Planck's Quantum Theory.
This theory can be simply stated as:
(i) Radiation is associated with energy.
(ii) Radiant energy is not emitted or absorbed continuously but discontinuously in the form of small packets of energy.
(iii) Each packet of energy is associated with a definite amount of energy and is known as quantum. In the case of light, the ‘quantum’ is known as ‘photon’.
(iv) The magnitude of quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of radiation.
E ∝ v
i.e. E = hv
where v = Frequency of radiation
h = Planck’s constant
= 6.625 x 10-34Js
(or 6.625 X 10-34 kg m2 s-1)
= 3.99 x 10-13 k Js mol-1
(v) A body can radiate or absorb energy in whole number multiples of a quantum i.e. nhv, where n = 1,2,3,4......etc.
Calculate the frequency and wavelength of light of wavelength:
(i) 5000 A (ii) 4.4 mμ (iii) 580 mm
(i) Wavelength of light, ![]()
Velocity of light, ![]()
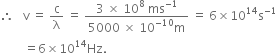
Wave number,
(ii) Wavelength of light,

Velocity of light c = 3 x 108 ms-1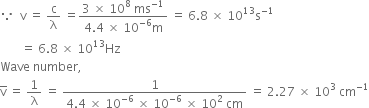
(iii) Wavelength of light, ![]() = 580 nm
= 580 nm
= 580 x 10-9m
Velocity of light, c = 3 x 108 ms-1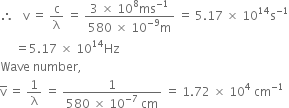
What is an emission spectra? What are its types?
When the radiation emitted from some source e.g. from the sun or by passing electric discharge through a gas at low pressure or by heating some substance to high temperature etc. is passed directly through the prism and recorded over a photographic plate or screen, the spectrum obtained is known as an emission spectrum.
Types of an emission spectrum. Emission spectra can be further divided into three types:
(i) Continuous spectrum. When white light from the sun or an electric bulb is analysed by passing through a prism, the spectrum obtained consists of a continuous band of seven colours from red to violet (like a rainbow). Such a spectrum is known as continuous spectrum. In such a spectrum, there is a continuous sequence of impressions in the form of colours.
(ii) Line spectrum. When the radiations emitted by the excited substances e.g. by placing some volatile salt (say NaCl) in the bunsen flame or by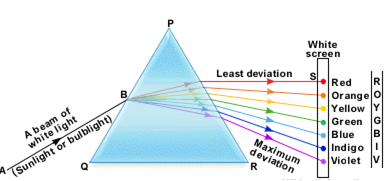
passing an electric discharge through a gas at low pressure are analysed by a spectrograph, discontinuous spectra consisting of a series of sharp lines and separated by dark bands is obtained. Such a spectrum consisting of parallel lines separated by dark space is called line spectrum. Line spectra is a finger -print of atoms because :
(a) each element has its characteristic spectrum, differing from those of all other elements and
(b) each line in the spectrum corresponds to a particular wavelength.
(iii) band spectrum. A molecule (unlike the atom) emits the radiations over a close range of wavelengths so that the spectrum consists of the group of lines spaced very close together. These lines are so much close that they look like a band. Such a spectrum is known as band spectrum.