Define matter. Briefly describe the physical classification (three different stages) of matter.
Matter. Matter is defined as anything which occupies space and has mass. On the basis of physical state, it has been classified as solids, liquids and gases.
(i) Solids are rigid substances which have definite shape and possess definite volume. For example, table, book, silver, wood etc.
(ii) Liquids are those mobile substances which have no definite shape but possess definite volume. They take up the shape of the vessel in which they are put. For example, milk, water, oil, mercury etc.
(iii) Gases are those mobile substances which have no fixed shape or volume. Gases flow to assume the shape of the container. For example, nitrogen, hydrogen, carbondioxide etc.
What do you know about the most scientific system of units?
Seven basic SI Units.
|
Quantity |
Unit |
Symbol |
|
Length |
metre |
m |
|
Mass |
kilogram |
kg |
|
Time |
second |
s |
|
Electric current |
ampere |
A |
|
Thermodynamic,Temperature |
kelvin |
K |
|
Amount of substance |
mole |
mol |
|
Luminous intensity |
Candela |
|
The rules for rounding off the non significant figures in the measurements are as under:
1. If the digit following the last digit to be retained is less than 5, the last digit is left unchanged. For example,
4·22 is rounded off to 4·2
4·14 is rounded off to 4·1
4·34 is rounded off to 4·3
2. If the last digit happens to be five (as in 4·335), then a digit before five is checked whether it is odd or even.
If it is odd, then it is increased by one. e.g.
4·335 is rounded off to 4·34
15·275 is rounded off to 15·28
If the digit before five is even, then it is retained as such. e.g.,
14·145 is rounded off to 14·14
6·225 is rounded off to 6·22
0·085 is rounded off to 0·08
3. If the last digit is greater than 5, the last-digit to be retained is increased by one. e.g.,
2·26 is rounded off to 2·3
4·68 is rounded off to 4·7
16·59 is rounded off to 16·6
What are the rules for determining the number of significant figures in answers involving:
(i) addition or subtraction
(ii) multiplication or division
(iii) calculations involving a number of steps?
(i) Addition or subtraction. While carrying out addition or subtraction of a number of terms, the result should be reported to the same number of decimal places as that of the term with the least number of decimal places.
(a) Addition of number. Ex. 3·5 g of NaCl and 4·23 g of KCI were dissolved in 25·001 g of water. What is the properly reported mass of solution?
Sol. +3·5 (this is the term with the least number of decimal place)
+ 4.23
+ 25.001
_______
Actual sum = 32.731 g
The respected sum should be only one decimal place after rounding off.
∴ Correct mass of the solution = 32·7 g
(b) Subtraction of number. Ex. Express the result of the following observations to the appropriate number of significant figures: 12·87 – 0·0107.
Sol. 12·87 (this is the term with the least number of decimal place)
-0.0107
________
Actual difference = 12.8693
The reported difference should be only upto two decimal places after rounding off.
∴ Reported difference = 12·87
(ii) Multiplication or division. While carrying out multiplication or division, the number of significant figures in the final result should not exceed the number of significant figures in the least precise factor.
(a) Multiplication of number
Ex. Complete the result of the following calculation to the appropriate number of significant figures:
87·4 × 0·00457
Sol. 87·4 × 0·00457 = 0·399418
As the number of significant figures in the least precise factor is three, therefore the reported result after rounding off is 0·399.
(b) Division of number.
Ex. Express the result of the following calculation to the appropriate number of significant figures:
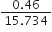
Sol. 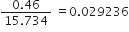
As the number of significant figures in the least precise factor is two (viz 0·46), therefore the reported result after rounding off is 0·029 (containing only two significant figures).
(iii) Calculations involing a number of steps: If a calculation involves a number of steps, the result should contain the same number of significant figures as that of the least precise number involved other than the exact numbers.
What do you mean by Dimensional Analysis (Derived units)?
From the seven basic or fundamental units, the units of some other physical quantities such as area, volume, pressure, force, speed, velocity etc. can be derived. These are called derived units. Derived unit of a physical quantity is also called dimensional formula of that quantity. For example, the unit of area can be derived as: Area = Length × Breadth If length = 6 m and breadth = 5m, then Area = 6m × 5m = 30m2
Unit for area is m2
Some common derived units are listed below:
Derived Units
|
Physical Quantity |
Units |
Symbol for Unit |
Definition in S.I. Basic Units |
|
Area |
square metre |
m2 |
m2 |
|
Volume |
cubic metre |
m3 |
m3 |
|
Density |
kilogram per cubic |
kg/m3 or kg m–3 |
|
|
Speed |
metre per second |
m/s or ms–1 |
|
|
Acceleration |
metre per second |
||
|
Force |
newton |
N |
kg ms–2 |
|
Pressure |
pascal |
Pa |
kg m–1s–1 or Nm–2 |
|
Energy |
joule |
J |
kg m2 s–2 |
|
Frequency |
hertz |
Hz |
s–1 |
|
Electric charge |
coulomb |
C |
A Sec = amp second |
|
Electric resistance |
ohm |
Ω |
m2 kg s–3 A–2 |
|
Electric potentialdifference |
volt |
V |
kg m2 s–3 A–1 or JA–1 S–1 |
