Balance the following equation: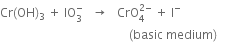
(i) The skeleton equation along with O.N. of each atom is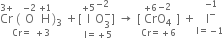
(ii) Noting the change in O.N. of the above atoms,
Increase Cr = +3 to +6 i.e. 3
Decrease 1 = +5 to -1 i.e. 6
(iii) Balancing the total increase in O.N. with a total decrease in O.N. by multiplying Cr(OH)3 by 2.
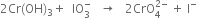
(iv) Balance Cr atoms by multiplying  by 2.
by 2.
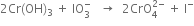
(v) Balance O atoms by adding OH- ion on the R.H.S.
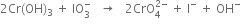
(vi) Balance H atoms by adding H2O and OH- ions as,
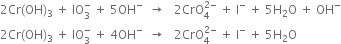
(i) The skeleton ionic equation is

(iii) Calculate the total increase and decrease in O.N.
Since there are two Cr atoms on L.H.S. and only one on R.H.S., therefore multiply Cr3+on R.H.S. of (1) by 2 and thus a total decrease in O.N. of Cr is 2 x 3 = 6.
(iv) Equalise the increase/decrease in O.N. by multiplying 
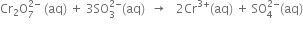
(v) Balance S atoms by multiplying 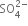 by 3.
by 3.

(vi) Balance O atoms by adding 4H2O molecules towards the R.H.S.
(vii) Balance H atoms by adding 8H ions on the L.H.S., since the reaction, occurs in the acidic medium.

Balance the following redox reaction by oxidation number method:
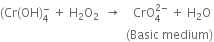
(i) The skeleton equation along with oxidation number of each atom is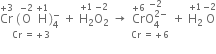
(ii) Noting the change in O.N. of above atoms,
Increase in Cr = + 3 to +6 i.e.
Decrease per atom of O = 1 (from O in H2O2 to O in H2O)
Total number of O atom involved = 2
Total decrease for 2 atoms of O = 2 x 1 = 2
(iii) Equalise the increase/decrease in O.N. by multiplying H2O2 by 3 and 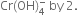
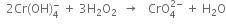
(iv) 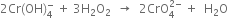
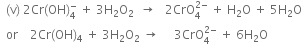
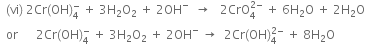
With the net ionic equation for the reaction of potassium dichromate (VI), K2Cr2O7 with sodium sulphite, Na2SO3, in an acid solution to give chromium (III) ion and the sulphate ion.
(i) The skeleton ionic equation is
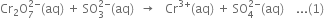
(ii) Write the O.N. of each atom and identify the atoms which undergo a change in O.N.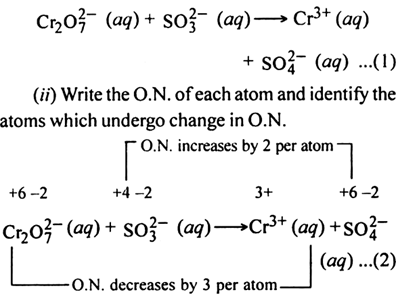
(iii) Calculate the total increase and decrease in O.N.
Since there are two Cr atoms on L.H.S. and only one on R.H.S., therefore multiply Cr3+on R.H.S. of (1) by 2 and thus a total decrease in O.N. of Cr is 2x3 = 6.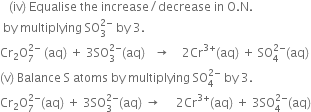
(vi) Balance O atoms by adding 4H2O molecules towards the R.H.S.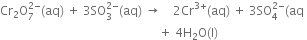
(vii) Balance H atoms by adding 8H ions on the L.H.S., since the reaction, occurs in the acidic medium.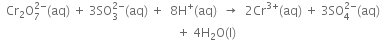
Balancing of equation of ion-electron method involves the following steps:
1. Identify oxidation and reduction half reactions in noting the change in oxidation number of atoms of different species in the reaction and write them separately.
2. Balance the atoms of all elements other than hydrogen and oxygen in both oxidation and reduction half reactions separately.
3. Now add required number of electrons (towards R.H.S. in oxidation half reaction and towards L.H.S. in reduction half reaction) in order to balance the charges of the atom undergoing oxidation or reduction on both the sides of the half reactions.
4. For a reaction taking place in an acidic or neutral medium, balance oxygen atoms by adding an H2O molecule for each oxygen atom on the side deficient in oxygen atoms in each half reaction and now balance hydrogen atom by adding H+ ion for each H atom on the side deficient in hydrogen.
5. If the reaction is carried in a basic solution, change each H+ ion to a water molecule and add an equal number of OH- ions to the opposite side of the equation.
6. Add the two balanced half equations and cancel any term common to both the sides.
