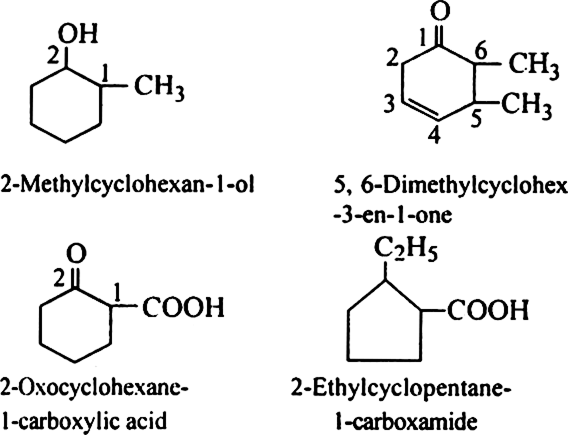
Discuss the rules for IUPAC nomenclature of compounds containing two or more functional groups.
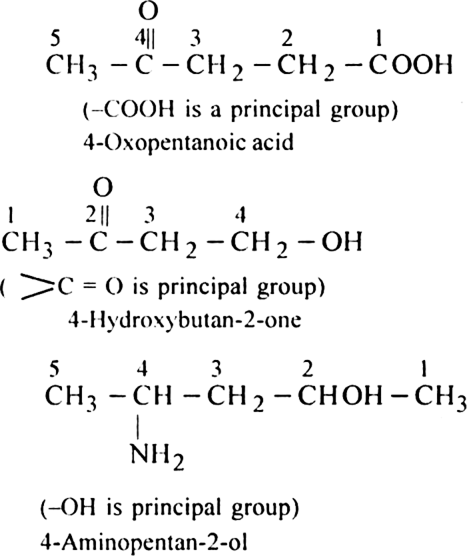
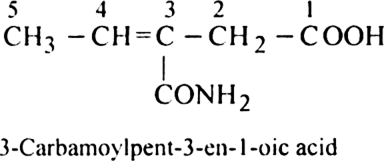
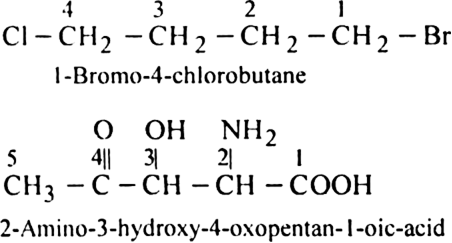
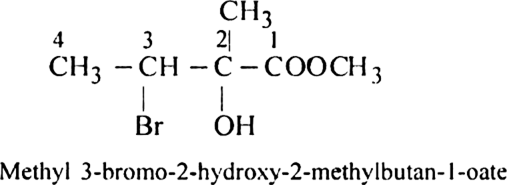
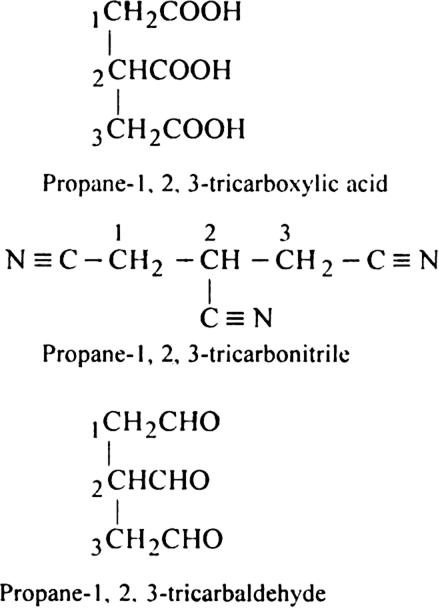
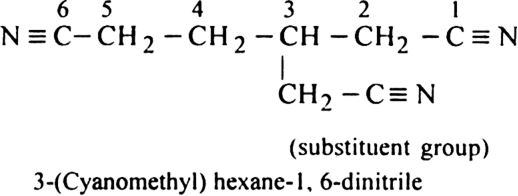
In naming the compounds containing double or triple bonds, the following rules are followed:
Rule 1. Select the longest continuous chain containing the carbon atoms carrying multiple bonds (double or triple). This gives the parent name of alkene or alkyne.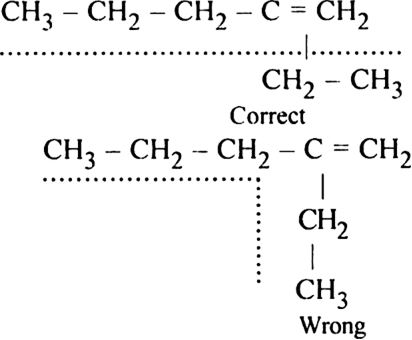
Rule 2. Once the longest chain is selected, the carbon atoms of the chain are numbered as 1,2,3......from one end to the other keeping in mind that the carbon atoms involved in multiple bonds should get a lowest possible number. For example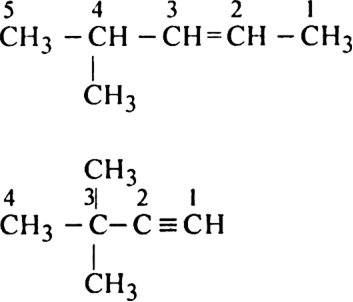
Rule 3. If the organic compound contains only one double bond or the triple bond, its locant on the positional number is always placed before its suffix, e.g.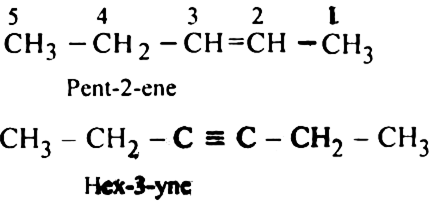
Rule 4. All the rules for naming side chains or substituents are then followed as in alkanes. e.g.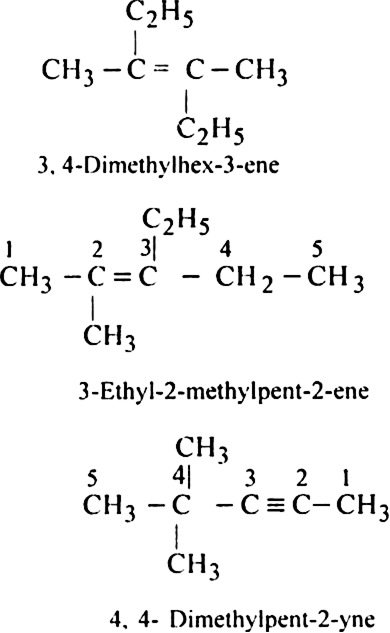
Rule 5. If there are more than one double bond in the molecule, their positions are indicated separately and the prefix (word root) is followed by a diene, a triene etc. e.g.![]()
Rule 6. If there are more than one triple bond in the molecule, their positions are indicated separately and the prefix (word root) is followed by a diene, triene, etc. e.g.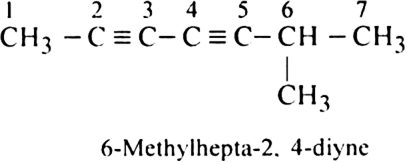
Rule 7. If both double and triple bonds are present, the numbering of the parent chain should always be done from that end which is nearer to the double or the triple bond (lowest sum for the multiple bonds must be followed).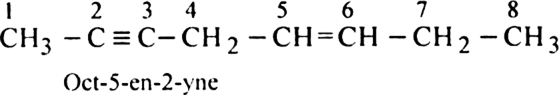
Rule 8. If the double bond and the triple bond are present at equal distances from the end of the chain, then double bond is always given the first preference over the triple bond in numbering, e.g.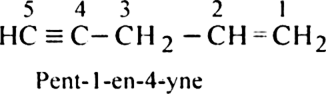
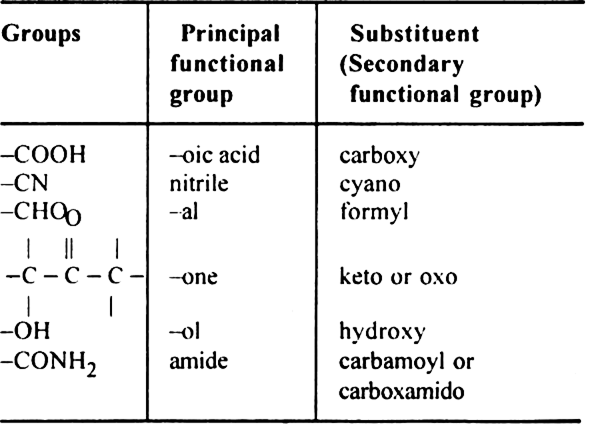
Discuss the rules for IUPAC nomenclature of compounds containing one functional group, multiple bonds and substituents.
(A) Lowest number for the functional group.
Rule. 1. Select the longest continuous chain containing the carbon atom having the functional group. e.g.
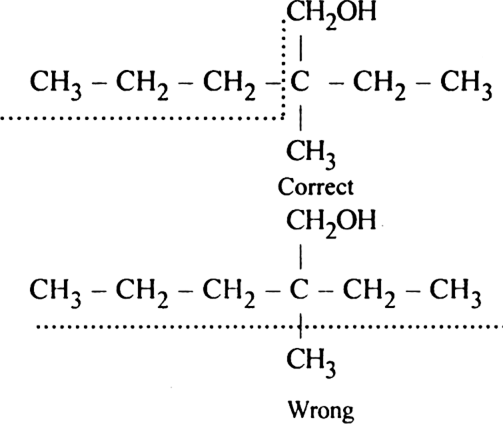
Rule 2. The numbering of atoms in the parent chain is done in such a way that the lowest number must be always given to the functional group e.g.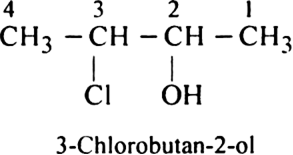
Rule 3. All the rules for naming side chains as substituents are then followed as in the case of alkanes.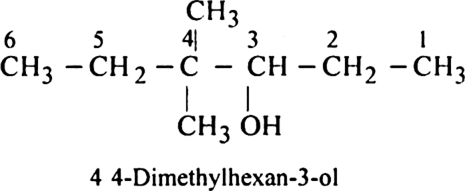
Rule 4. When a chain containing functional groups such as –CHO, – COOH, –COOR, – CONH2, –COCl, –C ≡ N etc. is present it is always given number 1 and number l is usually omitted from the final name of the compound.
Rule 5. If the organic compound contains a functional group, multiple bond, side chain or substituent, the following order of preference should be followed:
Functional group > Double bond or Triple bond > Substituent/side chain, e.g.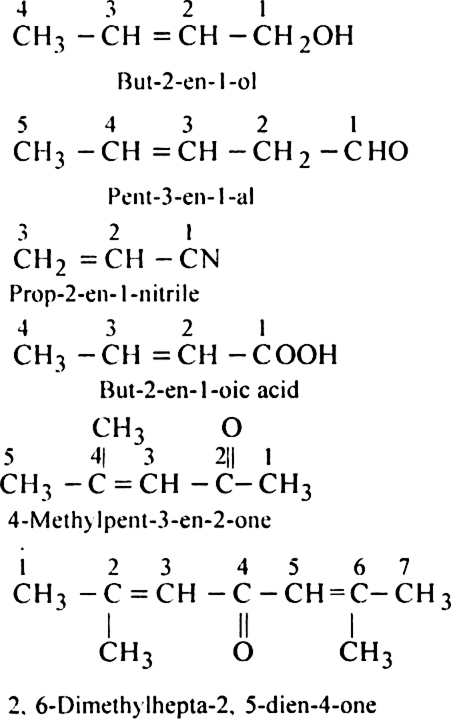
Rule 6. If the compound contains two or more like groups, the numerical prefixes di, tri, tetra etc. are used and the terminal ‘e’ from the primary suffix is retained.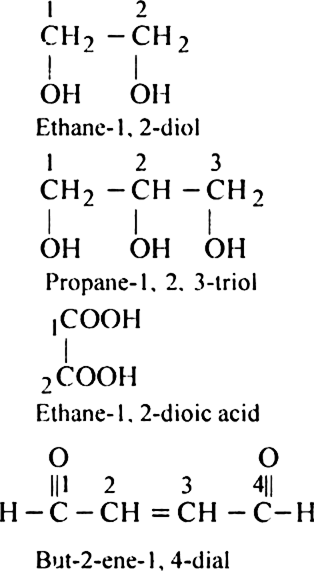
Discuss the rules for naming alicyclic compounds.
Rule 1. The name of alicyclic compounds is obtained by prefixing cyclo to the name of the corresponding straight-chain hydrocarbon (alkane, alkene or alkyne).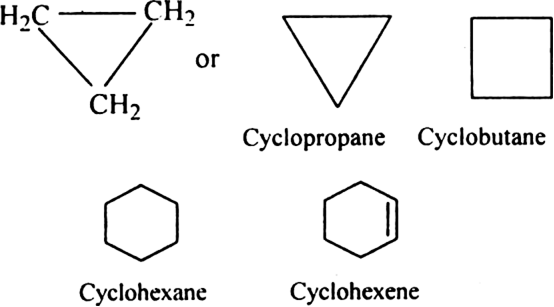
Rule 2. If one alkyl group is present, the same rules are applied as discussed earlier. For example.
Rule 3. If two or more alkyl groups or other substituent groups are present in the ring, their positions are indicated as 1,2, 3...... etc. While numbering the carbon atoms of the ring, the substituent which comes first in the alphabetical order is given the lowest number provided it does not violate the lowest sum rule. For example,
the order is given the lowest number provided it does not violate the lowest sum rule. For example,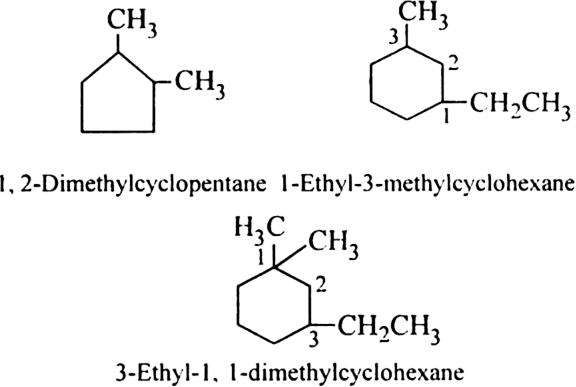
Rule 4. If the ring contains more equal number of carbon atom as the alkyl group attached to it, the compound is named as a derivative of cycloalkane and the alkyl group is treated as the substituent eroup. For example.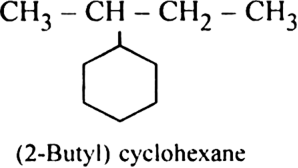
Rule 5. If the ring contains less number of carbon atoms as the alkyl group attached to it, the compound is named as a derivative of alkane and the cycloalky! group is taken as the substituent group.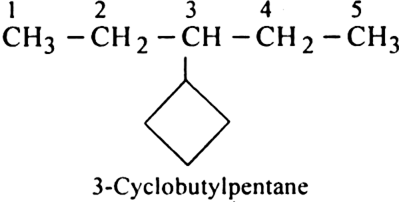
Rule 6. If some functional group is present in the ring, it is named as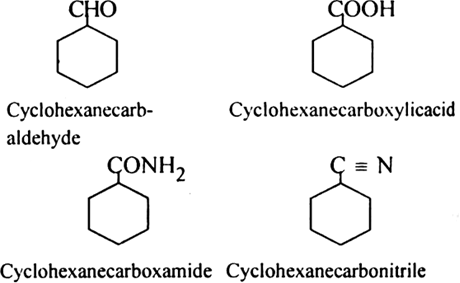
Rule 7. If the side chain contains a multiple bond or a functional group, the alicycli ring is treated as the substituent irrespective of the size of the ring. For example, 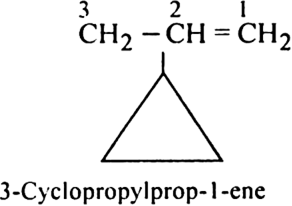
Rule 8. If a multiple (double or tiple) bond and some other substituents are present in the ring, the numbering is done in such a way that the multiple bond gets the lowest number. For example. 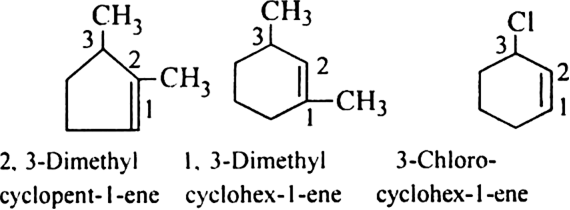
Rule 9. If some functional group along with other substituent groups is present in the ring, it is indicated by some appropriate prefix or suffix and its position is indicated by numbering the carbon atom of the ring in such a way that the functional group gets the lowest number.