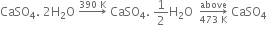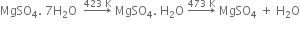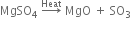What is Plaster of Paris? How is it prepared? What are its properties and uses?
Plaster of Paris is calcium sulphate hemihydrate.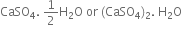
Preparation:
(i) From gypsum (CaSO4. 2H2O): When gypsum is heated to about 393 - 403 K, partial dehydration takes place with the formation of Plaster of Paris. 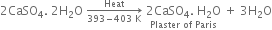
(ii) On a large scale, gypsum is gradually heated in a large steel vessel, holding several tonnes of material. This steel vessel is provided with a mechanical stirrer. During heating, the gypsum is stirred mechanically and the temperature is maintained between 393 - 403 K.
The temperature should be controlled carefully between 393 - 403 K, otherwise above this temperature (say 473 K), the whole of the water of hydration is lost and the gypsum gets dead burnt.
Properties:
(i) It is a white powder.
(ii) When mixed with water, Plaster of Paris quickly solidifies to gypsum with the evolution of heat and also expands slightly.
(iii) The action of heat: When plaster of Paris is heated at 473 K, it forms anhydrous calcium sulphate.
Uses. (i) It is used in surgery for plastering fractured parts of the body.
(ii) It is used for making casts for statues and for preparing blackboard chalks.
What is Gypsum? How is it prepared? What are its properties and uses?
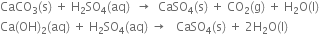

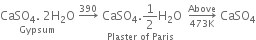
Discuss the composition and manufacturing details of cement.
Or
Mention the main constituents of Portland cement.
Cement is essentially a fine grind mixture of calcium aluminates and silicates which set to a hard mass when treated with water.
Composition. The average composition of Portland cement is
CaO 50-60% Fe2O3 1 - 2%
SiO2 20-25% MgO 2 - 3%
Al2O3 5-9% SO3 1 - 2%
Na2O 0.5 - 1%
Manufacturing details: Raw materials. Portland cement is made by fusing together two types of materials:
(i) Calcareous (or rich in lime) such as lime- stone, chalk, alkali waste.
(ii) Argillaceous (or rich in alumina or silica) such as clay, shale, slate etc.
The main raw materials for the manufacture of cement are first crushed separately in a suitable machine. They are then mixed together in required proportions and finely ground (pulverisation). The pulverised mass (either dry or in the formed slurry with water) is introduced into a rotary kiln. The kiln consists of a sheet steel cylinder about 150m in length and 4m in diameter lined inside with fire bricks. It rotates on its axis at the rate of 30-60 revolutions per minute. Due to the rotatory motion, the charge slowly moves down the kiln. A blast of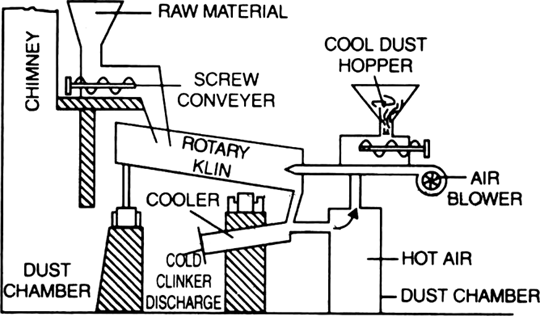
burning coal dust is blown into the kiln from the lower end. The charge takes 2-3 hours to travel from one end to the other. During its travel, the charge passes through various temperature zones and different reactions take place.
(a) In the upper portion of the kiln (up to 1100K): The material loses its moisture.
(b) In the middle portion (1100 to 1300K). Limestone decomposes to form calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
(c) At the lower end (1300 - 1800K). Lime and clay combine to form calcium silicate and calcium aluminate.
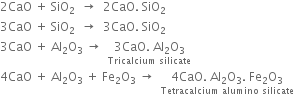
The hard mass thus formed is called clinker. The hot clinkers are cooled and mixed with 2 -3% gypsum and then finally powdered. The powdered material is known as cement and packed in jute or polyethene bags. Gypsum is added to retard the rate of setting of cement. Gypsum reacts with tricalcium aluminate to form calcium sulphoaluminate.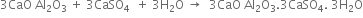
What is the effect of heat on the following compounds? (Write equations for the reactions):
(i) Calcium Carbonate
(ii) Magnesium chloride hexahydrate
(iii) Gypsum
(iv) Magnesium sulphate heptahydrate
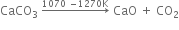
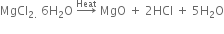
 which on heating above 473 K, changes into anhydrous calcium sulphate.
which on heating above 473 K, changes into anhydrous calcium sulphate.