
Explain the concept of motivation.
The concept of motivation focuses on explaining what moves behaviour. Most of our everyday explanation of behaviour is given in terms of motives. There may be a number of reasons for a particular behaviour. Motives also help in making predictions about behaviour. A person will work hard in schools, in sports, in business, in music and in many other situations, if he has a very strong need for an achievement. Hence, motives are the general states that enables us to make predictions about behaviour in many different situations.
What are the biological bases of hunger and thirst need?
Biological bases of hunger and thirst needs-Hunger: The stimuli of hunger include stomach contractions, which signify that the stomach is empty, a low concentration of glucose in the blood, a low level of protein and the amount of fats stored in the body. The liver also responds to the lack of bodily fuel by sending nerve impulses to the brain. The aroma, taste or appearance of food may also result in a desire to eat.
They all in combination act with external factors (such as taste, colour by observing other’s eating, and the smell of food, etc.) to the help one understands that she/he is hungry. Thus, it can be said that our food intake is regulated by a complex feeding satiety system located in the hypothalamus, liver and other parts of the body as well as the external cues available in the environment.
Thirst: When we are deprived of water for a period of several hours, the mouth and throat become dry, which leads to dehydration of body tissues. Drinking water is necessary to wet a dry mouth. The processes within the body itself control thirst and drinking of water. Water must get into the tissues sufficiently to remove the dryness of mouth and throat.
Motivation to drink water is mainly triggered by the conditions of the body: loss of water from cells and reduction of blood volume. When water is lost by bodily fluids, water leaves the interior of the cells. The anterior hypothalamus contains nerve cells called ‘osmoreceptors’, which generate nerve impulses in case of cell dehydration. These nerve impulses act as a signal for thirst and drinking.
Some researchers assume that the mechanism which explains the intake of water is also responsible for stopping the intake of water. Others have pointed out that the role of stimuli resulting from the intake of water in the stomach must have something to do with stopping of drinking water. However, the precise physiological mechanisms underlying the thirst drive are yet to be understood.
What is the basic idea behind Maslow’s hierarchy of needs? Explain with suitable examples.
Maslow proposed his view about human motivation. He attempted to portray a picture of human behaviour by arranging the various needs in a hierarchy. His viewpoint about motivation is popularly known as ‘Theory of self-actualisation’.
1. Maslow’s model can be conceptualised as a pyramid in which the bottom of this hierarchy represents basic physiological or biological needs which are basic to survival such as hunger, thirst etc. Only when these needs are met, the need to be free from threatened danger arises. This refers to the safety needs of physical and psychological nature.
2. Next comes the need to seek out other people, to love and to be loved. After these needs are fulfilled, the individual strives for esteem, i.e. the need to develop a sense of self-worth. The next higher need in the hierarchy reflects an individual’s motive towards the fullest development of potential, i.e., self-actualisation. A self-actualised person is self- aware, socially responsive, creative, spontaneous, open to novelty, and challenge. S/he also has a sense of humour and capacity for deep interpersonal relationships.
3. Lower level needs (physiological) in the hierarchy dominate as long as they are unsatisfied. Once they are adequately satisfied, the higher needs occupy the individual’s attention and effort. However, very few people reach the highest level because most people are concerned more with the lower level needs.
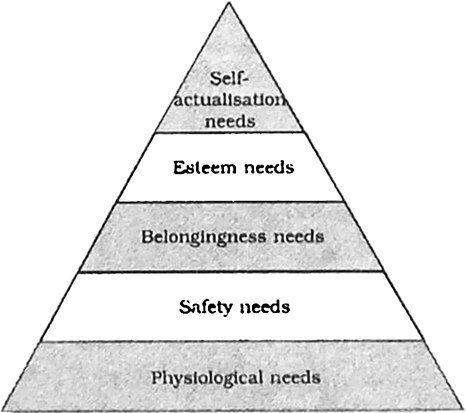
Fig: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
How do the needs for achievement, affiliation, and power influence the behaviour of adolescents? Explain with examples.
Needs for achievement, affiliation and power influence the behaviour of adolescents: Needs for achievement energies and directs behaviour as well as influences the perception of situations. During the formative years of social development, children acquire achievement motivation. They learn it from their parents, other role models, and socio-cultural influences. They have stronger than average desire for feedback on their performance, that is to know how they are doing, so that they can adjust their goals to meet the challenge.
Everybody need company or friend or want to maintain some form of relationship with others. Nobody likes to remain alone all the time. Formation of group is an important feature of human life. It involves motivation for social contact. Need for affiliation is aroused when individuals feel threatened or helpless and also when they are happy. People high on this need are motivated to seek the company of others and to maintain friendly relationships with other people.
Need for power is an ability of a person to produce intended effects on the behaviour and emotions of another person. The various goals of power motivation are to influence, control, persuade, lead and charm others.
Does physiological arousal precede or follow an emotional experience? Explain.
Yes, physiological arousal precede or follow an emotional experience. A great deal of physiological changes happen when we experience emotion. When we are excited, afraid or angry, these bodily changes might be relatively easily noted. While angry or existed about something, heart rate is increased, temples throbs, perspiration is increased, and limbs tremble.
Exact physiological changes that accompany emotions can be measured by sophisticated equipments. Both autonomic as well as somatic nervous system play important role in the emotional process. The experience of emotions is a result of a series of neuro physiological activations in which thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, and the cerebral cortex are involved significantly. Individuals with extensive injury in these brain areas have been known to demonstrate impaired emotional abilities. Selective activation of different brain areas has been experimentally shown to arouse different emotions in infants and adults.
