No, current will not be induced in the coil if the coil is rotated about it's axis.
Formula for flux is .
Two long parallel horizontal rails, distance d apart and each having a resistance A per unit length, are joined at one end by a resistance R. A perfectly conducting rod MN of mass m is free to slide along the rails without friction (see Fig.). There is a uniform magnetic field of induction B normal to the plane of the paper and directed into the paper. A variable force F is applied to the rod MN such that as the rod moves, constant current flows through R.
(i) Find the velocity of the rod and the applied force F as function of the distance x of the rod from R.
(ii) What fraction of the work done per second by F is converted into heat?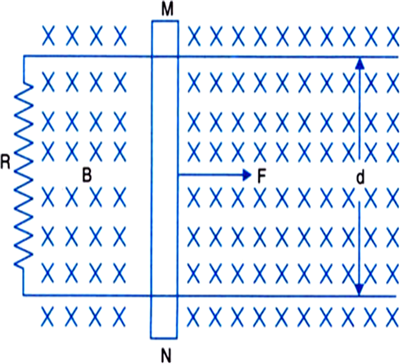
Given, two different coils.
L1 = 8 mH; L2 = 2 mH
a) Now, using the formula,
Hence, ratio of induced volatge is 4:1 .
b) Since,
Therefore,
Ratio of current is 1:4 .
c) Energy is given by,
Thus ratio of energy is 1 :4 .
