 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA baby has been born with a small tail. It is a case exhibiting
retrogressive evolution
mutation
atavism
metamorphosis
Given below is a pedigree chart of a family with five children. It shows the inheritance of attached ear-lobes as opposed to the free ones. The squares represent the male individuals and circles the female individuals. Which one of the following conclusions drawn is correct
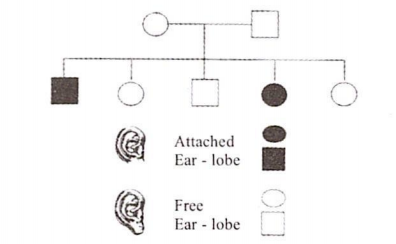
The parents are homozygous recessive.
The trait is Y-linked.
The parents are homozygous dominant.
The parents are heterozygous.
Given below is a representation of a kind of chromosomal mutation. What is the kind of mutation represented
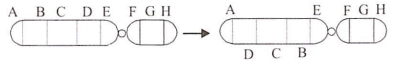
Deletion
Duplication
Inversion
Reciprocal translocation
How many different types of gametes can be formed by F1 progeny, resulting from the following cross
AA BB CC x aa bb cc
3
8
27
64
Assertion : In humans, the gamete contributed by the male determines whether the child produced will be male or female.
Reason : Sex in humans is a polygenic trait depending upon a cumulative effect of some genes on X chromosome and some on Y-chromosome.
If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
If both Assertion and Reason are false
One of the genes present exclusively on the X-chromosome in humans is concerned with
baldness
red-green colour blindness
facial hair/moustaches in males
night blindness
B.
red-green colour blindness
The most common form of red-green colour blindness is an 'X chromosome linked recessive' disorder. The 'red' and 'green' genes are known to reside at the tip of the long arm of the X chromosome. Women have two copies of the X-chromosome, and so they may have normal colour vision, even if they carry one copy of the defective gene. Men have only one X-chromosome, and so will be colour blind.
Mirabilis jalapa is an example of
complete dominance
supplementary gene
incomplete dominance
complementary gene
Which of the following is dominant character according to Mendel ?
Dwarf plant and yellow fruit
Terminal fruit and wrinkled seed
White testa and yellow pericarp
Green coloured fruit and rounded seed
Lack of independent assortment of genes A and B in fruit fly Drosophila is due to :
repulsion
linkage
crossing-over
recombination
When two mutations are located in the same functional unit or in different functional units, then it is confirmed by :
test cross
back cross
reciprocal cross
complementation test
