 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsA block is kept on a frictionless inclined surface with angle of inclination α. The incline is given an acceleration a to keep the block stationary. Then a is equal to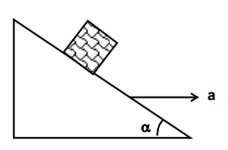
g/tanα
g cosecα
g
g
A body of mass m is accelerated uniformly from rest to a speed v in a time T. The instantaneous power delivered to the body as a function time is given by
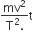
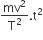
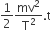
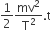
A particle moves in a straight line with retardation proportional to its displacement. Its loss of kinetic energy for any displacement x is proportional to
x2
ex
x
x
A ball is thrown from a point with a speed ν0 at an angle of projection θ. From the same point and at the same instant person starts running with a constant speed ν0/2 to catch the ball. Will the person be able to catch the ball? If yes, what should be the angle of projection?
yes, 60°
yes, 30°
no
no
A.
yes, 60°
Man will catch the ball if the horizontal component of velocity becomes equal to the constant speed of man i.e.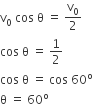
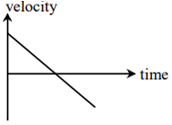
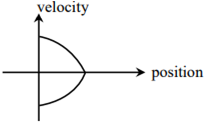
All the graphs below are intended to represent the same motion. One of them does it incorrectly. Pick it up.
The following figure gives the movement of an object. Select the correct statement from the given choices.
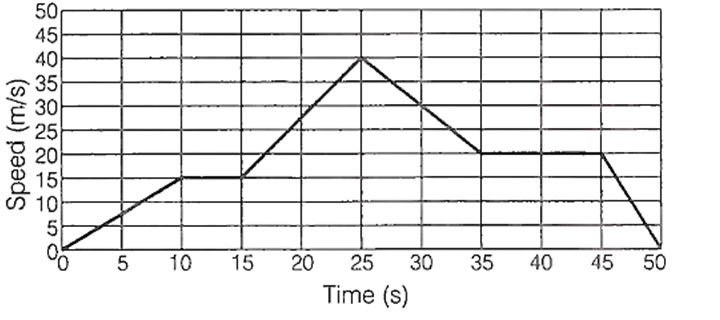
The total distance travelled by the object is 975 m
The maximum acceleration of the object is 2m/s2
The maximum deceleration happend between 25th and 85th seconds
The object was at rest between 10th and 15th seconds
Two object P and Q, travelling in the same direction starts from rest. While the object P starts at time t = 0 and object Q starts later at t = 30 min. The object P has an acceleration of 40 km/h2. To catch P at a distance of 20 km, the acceleration of Q should be
40 km/h2
80 km/h2
160 km/h2
120 km/h2
A train of length L move with a constant speed Vt. A person at the back of the train fires a bullet at time t = 0 towards a target which is at a distance of D (at time t = 0) from the front of the train (on the same direction of motion). Another person at the front of the train fires another bullet at time t = T towards the same target. Both bullets reach the target at the same time. Assuming the speed of the bullets Vb are same, the length of the train is
T × (Vb × 2Vt)
T × (Vb + Vt)
T × (Vb − 2Vt)
A person from a truck, moving with a constant speed of 60 km/h, throws a ball upwards with a speed of 60 km/h. Neglecting the effect of Earth and choose the correct answer from the given choice.
The person cannot catch the ball when it comes down since the truck is moving
The person can catch the ball when it comes down, if the truck is stopped immediately after throwing the ball
The person can catch the ball when it comes down, if the truck continues to move with a constant speed of 60 km/h
The person can catch the ball when it comes down, if the truck moves with speed more than 60 km/h
The x-t plot shown in the figure below describes the motion of the particle, along x-axis, between two positions A and B. The particle passes through two intermediate points P1 and P2 as shown in the figure
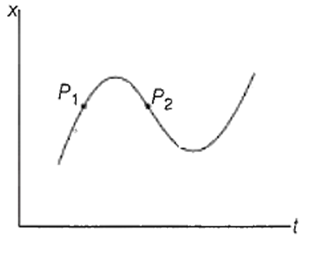
The instantaneous velocity is positive as P1 and negative at P2.
The instantaneous velocity is negative at both P1 and P2
The instantaneous velocity is negative at P1 and positive at P2
The instantaneous velocity is positive at both P1 and P2
