 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe compound that would produce a nauseating smell/ odour with a hot mixture of chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide is
PhCONH2
PhNHCH3
PhNH2
PhOH
The correct statement regarding the following compounds is
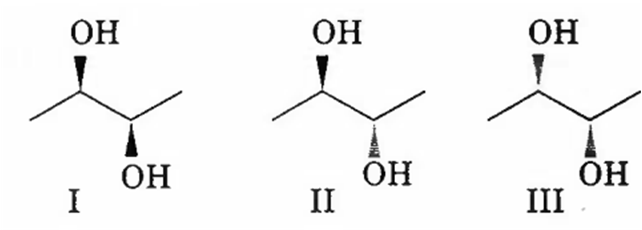
all three compounds are chiral
only I and II are chiral
I and III are diastereomers
only I and III are chiral
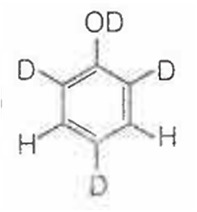
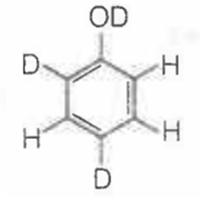
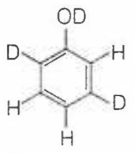
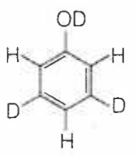
When phenol is treated with D2SO4 /D2O, some of the hydrogens get exchanged.The final product in this exchange reaction is
The correct order of acid strength of the following substituted phenols in water at 28°C is
p-nitrophenol < p-fluorophenol < p-chlorophenol
p-chlorophenol < p-fluorophenol < p-nitrophenol
p-fluorophenol < p-chlorophenol < p-nitrophenol
p-flurophenol < p-nitrophenol < p-chlorophenol
Correct statement(s) in cases of n-butanol and t-butanol is (are)
both are having equal solubility in water
t-butanol is more soluble in water than n-butanol
boiling point of t-butanol is lower than n-butanol
boiling point of n-butanol is lower than t-butanol
