 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsAn object 2.4 m in front of a lens forms a sharp image on a film 12 cm behind the lens. A glass plate 1cm thick, of refractive index 1.50 is interposed between lens and film with its plane faces parallel to film. At what distance (from lens) should object be shifted to be in sharp focus on film?
7.2 m
2.4 m
3.2 m
3.2 m
Let the xz-plane be the boundary between two transparent media. Medium 1 in z ≥ 0 has a refractive index of √2 and medium 2 with z<0 has a refractive index of √3. A ray of light in medium 1 given by the vector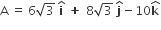 is incident on the plane of separation. The angle of refraction in medium 2 is
is incident on the plane of separation. The angle of refraction in medium 2 is
45°
60°
75°
75°
A car is fitted with a convex sideñview mirror of focal length 20 cm.Asecond car 2.8 m behind the first car is overtaking the first car at a relative speed of 15 m/s. The speed of the image of the second car as seen in the mirror of the first one is
1/15 m/s
10 m/s
15 m/s
15 m/s
A diverging lens with the magnitude of focal length 25 cm is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a converging lens of the magnitude of focal length 20 cm. A beam of parallel light falls on the diverging lens. The final image formed is
real and at a distance of 40 cm from the divergent lens
real and at a distance of 6 cm from the convergent lens
real and at a distance of 40 cm from the convergent lens
real and at a distance of 40 cm from the convergent lens
In an optics experiment, with the position of the object fixed, a student varies the position of a convex lens and for each position, the screen is adjusted to get a clear image of the object. A graph between the object distance u and the image distance v, from the lens, is plotted using the same scale for the two axes. A straight line passing through the origin and making an angle of 45o with the x-axis meets the experimental curve at P. The coordinates of P will be
(2f, 2f)
(f/2, f/2)
(f,f)
(f,f)
A student measures the focal length of the convex lens by putting an object pin at a distance ‘u’ from the lens and measuring the distance ‘v’ of the image pin. The graph between ‘u’ and ‘v’ plotted by the student should look like
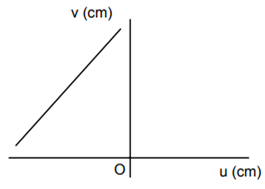
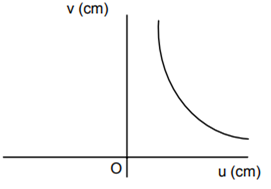
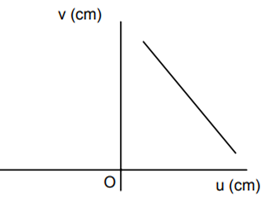

An experiment is performed to find the refractive index of glass using a travelling microscope. In this experiment distance are measured by
a vernier scale provided on the microscope
a standard laboratory scale
a meter scale provided on the microscope
a meter scale provided on the microscope
Two lenses of power -15D and +5D are in contact with each other. The focal length of the combination is
-20 cm
-10 cm
+20 cm
+20 cm
A plane convex lens of refractive index 1.5 and radius of curvature 30 cm is silvered at the curved surface. Now this lens has been used to form the image of an object. At what distance from this lens an object be placed in order to have a real image of the size of the object?
20 cm
30 cm
60 cm
60 cm
The angle of incidence at which reflected light totally polarized for reflection from air to glass (refractive index n), is
sin−1 (n
sin−1 (1/n)
tan−1 (1/n)
tan−1 (1/n)
