 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA consumer consumes only two goods. Explain consumer's equilibrium with the help of utility analysis.
State the behaviour of marginal product in the law of variable proportions. Explain the causes of this behaviour.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeExplain the conditions of consumer's equilibrium with the help of the indifference curve analysis.
From the following information about a firm, find the firms equilibrium output in terms of marginal cost and marginal revenue. Give reasons. Also find profit at this output.
|
Output (units) |
Total Revenue (Rs.) |
Total Cost (Rs.) |
|
1 |
7 |
8 |
|
2 |
14 |
15 |
|
3 |
21 |
21 |
|
4 |
28 |
28 |
|
5 |
35 |
36 |
Market of a commodity is in equilibrium. Demand for the commodity 'increases'. Explain the chain of effects of this change till the market again reaches equilibrium. Use diagram.
An increase in the demand for the commodity leads to an increase in the equilibrium price and quantity.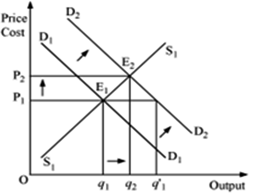
Here,
D1D1 and S1S1 represent the market demand and market supply respectively. The initial equilibrium occurs at E1, where the demand and the supply intersect each other. Due to the increase in the demand for the commodity, the demand curve will shift rightward parallel fromD1D1 to D2D2, while the supply curve will remain unchanged. Hence, there will be a situation of excess demand, equivalent to (q1' − q1). Consequently, the price will rise due to excess demand. The price will continue to rise until it reaches E2 (new equilibrium), where D2D2 intersects the supply curve S1S1. The equilibrium price increases from P1 to P2 and the equilibrium output increases from q1 to q2.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type