 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Complete the following chemical equation
(i) Cu + HNO3 (dilute) --->
(ii) XeF4 + O2F2 -->
(b) Explain the following observation:
(i) Phosphorus has a greater tendency for catenation than nitrogen.
(ii) Oxygen is a gas but sulphur a solid.
(iii) The halogens are coloured. Why?
a) Define the following terms:
(i) Mole fraction
(ii) Ideal solution
(b) 15.0 g of an unknown molecular material is dissolved in 450 g of water. The resulting solution freezes at - 0.34°C. What is the molar mass of the material? (Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol-1)
(i) Mole fraction: The mole fraction of a component in a mixture is defined as the ratio of the number of moles of the component to the total number of moles of all the components in the mixture. Mathematically, it is represented as:

Mole fraction is denoted by ‘x’.
(ii) Ideal Solution:
Solutions which obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentrations are known as ideal solution. Along with that for ideal solution:
Enthalpy of mixing of the pure components to form the solution i.e mix H = 0 and volume of mixing, mix V = 0.
An ideal solution will be formed when intermolecular forces of attraction between the molecules of solute (A - A) and those between the molecules of solvent (B -B) are nearly equal to those between solute and solvent molecules (A - B).
For Example: n-Hexane and n-heptane
(b) Given mass of solute = wb = 15.0g
Molar mass of solute = Mb =?
Mass of water = wa = 450 g
Freezing point of water = 0°C = 273 K
Freezing point of solution = - 0.34°K
= (- 0.34 + 273) K
Depression in freezing point = Tf= 273 - (-0.34 + 273)
= 0.34 K
Kf for water = 1.86 K Kg mol-1
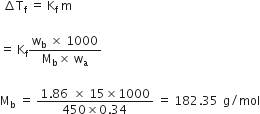
(a) Explain the following:
(i) Henry’s law about the dissolution of a gas in a liquid.
(ii) Boiling point elevation constant for a solvent.
(b) A solution of glycerol (C3H8O3) in water was prepared by dissolving some glycerol in 500 g of water. This solution has a boiling point of 100.42°C. What mass if glycerol was dissolved to make this solution? (Kb for water = 0.512 K kg mol-1)
(a) Write a suitable chemical equation to complete each of the following transformations:
(i) Butan-1-ol to butanoic acid
(ii) 4-methylacetophenone to benzene-1, 4-dicarboxylic acid
(b) An organic compound with molecular formula C9H10O forms 2, 4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollen’s reagent and undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1, 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound.
(a) Give chemical tests to distinguish between
(i) Propanol and propanone
(ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
(b) Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of their property as indicated:
(i) Acetaldeyde, Acetone, Methyl tert-butyl ketone (reactivity towards HCN)
(ii) Benzoic acid, 3, 4-Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxybenzoic acid (acid strength).
(iii) CH3CH2CH (Br) COOH, CH3CH (Br) CH2COOH, (CH3)2CHCOOH (acid strength)
