 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeState the different phases of changes in Total Product and Marginal Product in the Law of Variable Proportions. Also show the same in a single diagram.
Why is the equality between marginal cost and marginal revenue necessary for a firm to be in equilibrium? Is it sufficient to ensure equilibrium? Explain.
Equilibrium refers to a state of rest when no change is required. A firm (producer) is said to be in equilibrium when it has no inclination to expand or to contract its output. This state either reflects maximum profits or minimum losses.
According to MC=MR approach, As long as MC is less than MR, it is profitable for the producer to go on producing more because it adds to its profits. He stops producing more only when MC becomes equal to MR.
When MC is greater than MR after equilibrium, it means producing more will lead to decline
in profits.
Both the conditions are needed for Firm’s Equilibrium: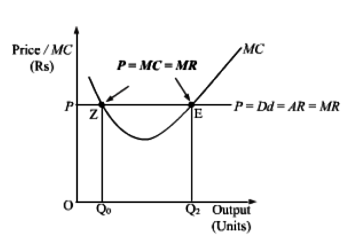
1. MC = MR:
MR is the addition to TR from sale of one more unit of output and MC is addition to TC for
increasing production by one unit. Every producer aims to maximize the total profits. For
this, a firm compares it’s MR with its MC. Profits will increase as long as MR exceeds MC
and profits will fall if MR is less than MC. So, equilibrium is not achieved when MC < MR
as it is possible to add to profits by producing more. Producer is also not in equilibrium
when MC > MR because benefit is less than the cost. It means, the firm will be at
equilibrium when MC = MR.
2. MC is greater than MR after MC = MR output level:
MC = MR is a necessary condition, but not sufficient enough to ensure equilibrium. Only
that output level is the equilibrium output when MC becomes greater than MR after the
equilibrium.
It is because if MC is greater than MR, then producing beyond MC = MR output will reduce
profits. On the other hand, if MC is less than MR beyond MC = MR output, it is possible to
add to profits by producing more. So, first condition must be supplemented with the
second condition to attain the producer’s equilibrium.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. The demand for the good 'increases'. Explain the chain of effects of this change.
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsBorrowing in government budget is
Revenue deficit
Fiscal deficit
Primary deficit
Primary deficit
Other things remaining unchanged, when in a country the price of foreign currency
rises, national income is (choose the correct alternative)
Likely to rise
Likely to fall
Likely to rise and fall both
Likely to rise and fall both
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeIf Real GDP is Rs. 200 and Price Index (with base = 100) is 110, calculate Nominal GDP.
Name the broad categories of transactions recorded in the 'capital account' of the Balance of Payments Accounts.
OR
Name the broad categories of transactions recorded in the 'current account' of the Balance of Payments Accounts.
