 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeState the different phases of changes in Total Product and Marginal Product in the Law of Variable Proportions. Also show the same in a single diagram.
Why is the equality between marginal cost and marginal revenue necessary for a firm to be in equilibrium? Is it sufficient to ensure equilibrium? Explain.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. The demand for the good 'increases'. Explain the chain of effects of this change.
Equilibrium is defined as a situation where the plans of all consumers and firms in the market match and the market clears. When the supply and demand curves intersect, the market is in equilibrium. This is where the quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. The corresponding price is the equilibrium price or market-clearing price, the quantity is the equilibrium quantity.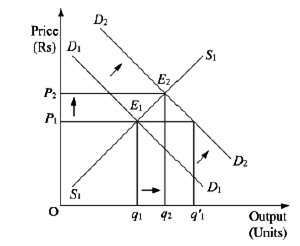
Suppose D1 and S1 are the initial market demand curve and the initial market supply curve, respectively. The initial equilibrium is established at point E1, where the market demand curve and the market supply curve intersects each other. Accordingly, the equilibrium price is OP1 and the equilibrium quantity demanded is Oq1.
Now, if there is an increase in the market demand, the market demand curve shifts parallely rightwards to D2 from D1, while the market supply curve remains unchanged at S1. This implies that at the initial price OP1, there exist excess demand equivalent to (Oq'1 - Oq1) units. This excess demand will increase competition among the buyers and they will now be ready to pay a higher price to acquire more units of the good. This will further raise the market price. The price will continue to rise till it reaches OP2. The new equilibrium is established at point E2, where the new demand curve D2 intersects the supply curve S1.
Hence, an increase in demand with supply remaining constant, results in rise in the equilibrium price as well as the equilibrium quantity.
 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsBorrowing in government budget is
Revenue deficit
Fiscal deficit
Primary deficit
Primary deficit
Other things remaining unchanged, when in a country the price of foreign currency
rises, national income is (choose the correct alternative)
Likely to rise
Likely to fall
Likely to rise and fall both
Likely to rise and fall both
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeIf Real GDP is Rs. 200 and Price Index (with base = 100) is 110, calculate Nominal GDP.
Name the broad categories of transactions recorded in the 'capital account' of the Balance of Payments Accounts.
OR
Name the broad categories of transactions recorded in the 'current account' of the Balance of Payments Accounts.
