 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeState different phases of the law of variable proportions on the basis of total product. Use diagram.
Or
Explain the geometric method of measuring price elasticity of supply. Use diagram.
Law of variable proportion:
Law of variable proportion states that as more of the variable factor input is combined with the fixed factor input, a point will eventually be reached where the marginal product of the variable factor input starts declining.
| units of fixed factor | units of variable factors | total product |
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
4 12 24 32 34 34 30 21 10 |
Stage I: As more units of factor input are used, the total product increases at an increasing rate which is called increasing returns to the factor input.
Stage II: However, when the 4th unit of factor input is used, the diminishing returns sets in, where TP increases at a decreasing rate.
Stage III: TP starts declining from 34 to 10 when the 9th unit is employed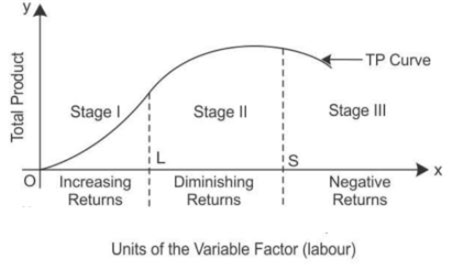
or,
Geometric method measures elasticity at a given point on the supply curve and is also know as ‘Arc method’ or Point method’. this method is a graphical presentation of the elasticity of the supply. the degree of the price elasticity of supply depends on the slope and origin position of the supply curve. There are five possible situations in the elasticity of supply curve.
(a)unitary elasticity of supply (E=1) : where if the straight line supply curve originates from the origin, then the angle of inclination of supply curve, the elasticity of supply will always be equal to one i.e E=1 this supply curve is called unitary elastic supply curve.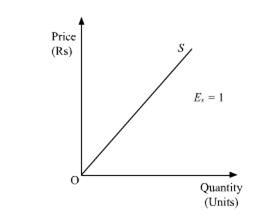
(b)less elastic supply (E<1) where if the supply curve originates from the horizontal intercept of quantity axis, then the angle of inclination of supply curve, the elasticity of the supply curve will be less than one i.e (E<1).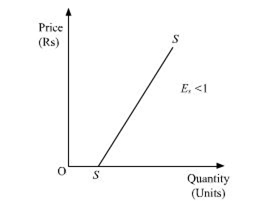
(c) more elastic supply (E>1) the more elastic supply curve originates from the vertical intercept of price axis. the value of elasticity of supply originates from the vertical intercept is greater than one i.e (E>1)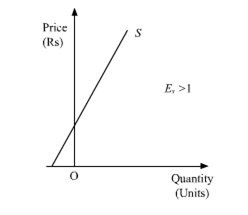
Good Y is a substitute of good X. The price of Y falls. Explain the chain of effects of this change in the market of X.
Or
Explain the chain of effects of excess supply of a good on its equilibrium price.
Given below is the cost schedule of a product produced by a firm. The market price per unit of the product at all levels of output is Rs. 12. Using marginal cost and marginal revenue approach, find out the level of equilibrium output. Give reasons for your answer :
| output (units) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| average cost (in RS) | 12 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10.4 | 11 |
The ratio of total deposits that a commercial bank has to keep with Reserve Bank of India is called : (choose the correct alternative)
(a) Statutory liquidity ratio
(b) Deposit ratio
(c) Cash reserve ratio
(d) Legal reserve ratio
Aggregate demand can be increased by : (choose the correct alternative)
(a) increasing bank rate
(b) selling government securities by Reserve Bank of India
(c) increasing cash reserve ratio
(d) none of the above
