 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeState the law of radioactive decay.
Plot a graph showing the number (N) of undecayed nuclei as a function of time (t) for a given radioactive sample having half-life T½.
Depict in the plot the number of undecayed nuclei at (i) t = 3 T½ and (ii) t = 5 T½. Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(i) With the help of a labelled diagram, describe briefly the underlying principle and working of a step up transformer.
(ii) Write any two sources of energy loss in a transformer.
(iii) A step up transformer converts a low input voltage into a high output voltage.
Does it violate law of conservation of energy? Explain.
Derive an expression for the impedance of a series LCR circuit connected to an AC supply of variable frequency.
Plot a graph showing variation of current with the frequency of the applied voltage.
Explain briefly how the phenomenon of resonance in the circuit can be used in the
Tuning mechanism of a radio or a TV set.(a) Draw a ray diagram to show refraction of a ray of monochromatic light passing through a glass prism.
Deduce the expression for the refractive index of glass in terms of angle of prism and angle of minimum deviation.
(b) Explain briefly how the phenomenon of total internal reflection is used in fiber optics.
a) The phenomenon of refraction for a ray of monochromatic light passing through a glass prism is shown as below: 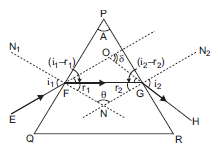
Let, PQR be the principal section of the prism.
The refracting angle of prism is A. Monochromatic light EF is incident on face PQ at angle of incidence i1. This ray enters from a rarer to denser medium and hence is refracted towards the normal FN. Refracted ray is FG. Angle of refraction for this face is r1. Refracted ray FG becomes incident on face PR and is refracted away from the normal GN2 and emerges in the direction GH. The angle of incidence on this face is r2 (into prism) and angle of refraction (into air) is i2. At point O, incident and the emergent ray meet. The angle between these two rays is called the angle of deviation ‘ ’.
’. 
 .
.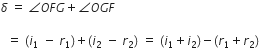 ... (1)
... (1)
The normal FN1 and GN2 on faces PQ and PR respectively, when produced meet at N.
Let, 
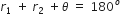 ... (2)
... (2) 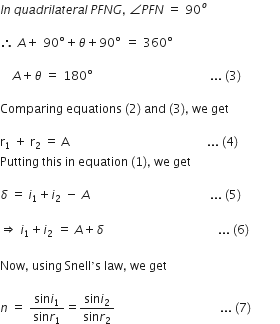
We can see that, for one angle of deviation we have two angles of incidence. But, angle of deviation is minimum for only one particular angle if incidence. Angle of minimum deviation is denoted by 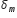 .
.
So let, i1 = i2 = i
And r1 = r2 = r
Therefore, we have (4) and (6), we have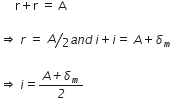
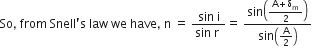
b) An optical fiber is a device based on total internal reflection by which a light signal may be transmitted from one place to another with a negligible loss of energy. When a light ray is incident on one end at a small angle of incidence, it suffers refraction from air to quartz and strikes the quartz-coating interface at an angle more than the critical angle. Hence, total internal reflection happens and the ray of light strikes the opposite face again at an angle greater than critical angle. The phenomenon of total internal reflection takes place. Thus the ray within the fiber suffers multiple total internal reflections and finally strikes the other end at an angle less than critical angle for quartz-air interface and emerges in air.
(a) Obtain lens makers formula using the expression
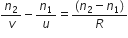
Here the ray of light propagating from a rarer medium of refractive index (n1) to a denser medium of refractive index (n2) is incident on the convex side of spherical refracting surface of radius of curvature R.
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation by a concave mirror when the object is kept between its focus and the pole. Using this diagram, derive the magnification formula for the image formed.
