 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type(i) Explain with the help of a diagram the formation of depletion region and barrier potential in a p-n junction.
(ii) Draw the circuit diagram of a half wave rectifier and explain its working.
(i) Which mode of propagation is used by shortwave broadcast services having frequency range from a few MHz upto 30 MHz ? Explain diagrammatically how long distance communication can be achieved by this mode.
(ii) Why is there an upper limit to frequency of waves used in this mode?
For a CE-transistor amplifier, the audio signal voltage across the collector resistance of 2 k is 2 V. Suppose the current amplification factor of the transistor is 100, find the input signal voltage and base current, if the base resistance is 1 kV.
is 2 V. Suppose the current amplification factor of the transistor is 100, find the input signal voltage and base current, if the base resistance is 1 kV.
Define the term wave front. State Huygen’s principle.
Consider a plane wave front incident on a thin convex lens. Draw a proper diagram to show how the incident wave front traverses through the lens and after refraction focusses on the focal point of the lens, giving the shape of the emergent wave front.
OR
Explain the following, giving reasons :
(i) When monochromatic light is incident on a surface separating two media, the reflected and refracted light both have the same frequency as the incident frequency.
ii) When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, the speed decreases. Does this decrease in speed imply a reduction in the energy carried by the wave?
(iii) In the wave picture of light, intensity of light is determined by the square of the amplitude of the wave. What determines the intensity in the photon picture of light?
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(i) Draw a labelled diagram of a step-down transformer. State the principle of its working.
(ii) Express the turn ratio in terms of voltages.
(iii) Find the ratio of primary and secondary currents in terms of turn ratio in an ideal transformer.
(iv) How much current is drawn by the primary of a transformer connected to 220 V supply when it delivers power to a 110 V- 550 W refrigerator?
(a) Explain the meaning of the term mutual inductance. Consider two concentric circular coils, one of radius r1 and the other of radius r2 (r1 < r2) placed coaxially with centres coinciding with each other. Obtain the expression for the mutual inductance of the arrangement.
(b) A rectangular coil of area A, having number of turns N is rotated at ‘ f ’ revolutions per second in a uniform magnetic field B, the field being perpendicular to the coil. Prove that the maximum emf induced in the coil is 2 f NBA.
f NBA.
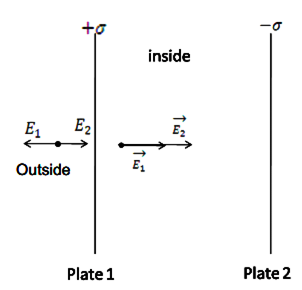
(i) Use Gauss’s law to find the electric field due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet. What is the direction of field for positive and negative charge densities?
(ii) Find the ratio of the potential differences that must be applied across the parallel and series combination of two capacitors C1 and C2 with their capacitances in the ratio 1 : 2 so that the energy stored in the two cases becomes the same.
(i) If two similar large plates, each of area A having surface charge densities 1s and 2s are separated by a distance d in air, find the expressions for
(a) field at points between the two plates and on outer side of the plates. Specify the direction of the field in each case.
(b) the potential difference between the plates.
(c) the capacitance of the capacitor so formed.
(ii) Two metallic spheres of radii R and 2R are charged so that both of these have same surface charge density s. If they are connected to each other with a conducting wire, in which direction will the charge flow and why ?
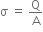
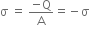
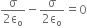
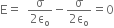
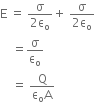
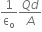
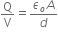
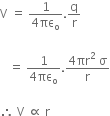
(i) Derive the mathematical relation between refractive indices n1 and n2 of two radii and radius of curvature R for refraction at a convex spherical surface. Consider the object to be a point since lying on the principle axis in rarer medium of refractive index n1 and a real image formed in the denser medium of refractive index n2. Hence, derive lens maker’s formula.
(ii) Light from a point source in air falls on a convex spherical glass surface of refractive index 1.5 and radius of curvature 20 cm. The distance of light source from the glass surface is 100 cm. At what position is the image formed ?
(a) Draw a labelled ray diagram to obtain the real image formed by an astronomical telescope in normal adjustment position. Define its magnifying power.
(b) You are given three lenses of power 0.5 D, 4 D and 10 D to design a telescope.
(i) Which lenses should he used as objective and eyepiece ? Justify your answer.
ii) Why is the aperture of the objective preferred to be large?
