 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions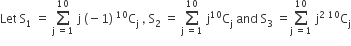
Statement-1: S3 = 55 × 29.
Statement-2: S1 = 90 × 28 and S2 = 10 × 28.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true; statement-2 is not a correct explanation for Statement-1.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false.
C.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false.
Consider the system of linear equation
x1 + 2x2 + x3 = 3
2x1 + 3x2 + x3 = 3
3x1 + 5x2 + 2x3 = 1
The system has
infinite number of solutions
exactly 3 solutions
a unique solution
a unique solution
let f : (-1, 1) → R be a differentiable function
with f(0) = -1 and f'(0) = 1.
Let g(x) = [f(2f(x) + 2)]2. Then g'(0) =
4
-4
0
0
Let A be a 2 × 2 matrix with non-zero entries and let A2 = I, where I is 2 × 2 identity matrix. Define Tr(A) = sum of diagonal elements of A and |A| = determinant of matrix A.
Statement-1: Tr(A) = 0.
Statement-2: |A| = 1.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true; statement-2 is not a correct explanation for Statement-1.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false.
Let f : R → R be a continuous function defined
by f(x) = 1/ex + 2e-x
Statement - 1: f(c) = 1/3, for some c ∈ R.
Statement-2: 0 < f(x)≤ 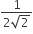 , for all x ∈ R.
, for all x ∈ R.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is true; statement-2 is not a correct explanation for Statement-1.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false.
Statement-1 is true, Statement-2 is false.
The equation of the tangent to the curve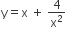 , that is parallel to the x-axis, is
, that is parallel to the x-axis, is
y = 0
y = 1
y = 3
y = 3
If two tangents drawn from a point P to the parabola y2= 4x are at right angles, then the locus of P is
X = 1
2x +1 = 0
x = -1
x = -1
The number of 3 × 3 non-singular matrices, with four entries as 1 and all other entries as 0, is
less than 4
5
6
6
Let f : R → R be defined by 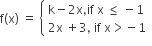
If f has a local minimum at x = - 1 then a possible value of k is
1
0
-1/2
-1/2
