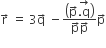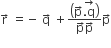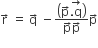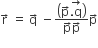Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsThe population p(t) at time t of a certain mouse species satisfies the differential equation┬Ā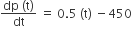 . if p (0) = 850, then the ┬Ātime at which the population becomes zero is
. if p (0) = 850, then the ┬Ātime at which the population becomes zero is
2 log 18
log 9
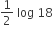
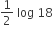
Let a, b Ōłł R be such that the function f given by f(x) = ln |x| + bx
2+ ax, x ŌēĀ 0 has extreme values at x = ŌĆō1 and x = 2.
Statement 1: f has local maximum at x = ŌĆō1 and at x = 2.
Statement 2:┬Ā
Statement 1 is false, statement 2 is true
Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is a correct explanation for statement 1
Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1
Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1
If: R┬ĀŌåÆR is a function defined by┬Ā ┬Āwhere [x] denotes the greatest integer function, then f is
┬Āwhere [x] denotes the greatest integer function, then f is
continuous for every real x
discontinous only at x = 0
discontinuous only at non-zero integral values of x
discontinuous only at non-zero integral values of x
Let P and Q be 3 ├Ś 3 matrices with P ŌēĀ Q. If P3= Q3┬Āand P2Q = Q2P, then determinant of(P2+ Q2) is equal to
-2
1
0
0
Consider the function f(x) = |x ŌĆō 2| + |x ŌĆō 5|, x Ōłł R.
Statement 1: fŌĆ▓(4) = 0
Statement 2: f is continuous in [2, 5], differentiable in (2, 5) and f(2) = f(5).
Statement 1 is false, statement 2 is true
Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is a correct explanation for statement 1
Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1
Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true; statement 2 is not a correct explanation for statement 1
Let┬Ā ┬Ābe ┬Ātwo unit vectors. If the vectors┬Ā
┬Ābe ┬Ātwo unit vectors. If the vectors┬Ā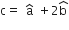 ┬Āand┬Ā
┬Āand┬Ā ┬Āare perpendicular┬Āto each other, then the angle between┬Ā
┬Āare perpendicular┬Āto each other, then the angle between┬Ā ┬Āis┬Ā
┬Āis┬Ā
ŽĆ/6
ŽĆ/2
ŽĆ/3
ŽĆ/3
If the integral┬Ā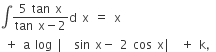 ┬Ā then an equal to┬Ā
┬Ā then an equal to┬Ā
-1
-2
1
1
D.
1

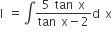
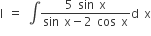
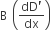
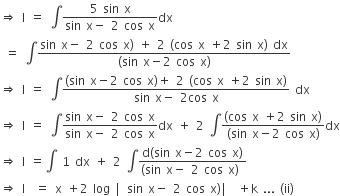
| ŌćÆ |
Assuming the balls to be identical except for difference in colours, the number of ways in which one or more balls can be selected from 10 white, 9 green and 7 black balls is
880
629
630
630
Let ABCD be a parallelogram such that  ┬Āand┬ĀŌłĀBAD be an acute angle. If┬Ā
┬Āand┬ĀŌłĀBAD be an acute angle. If┬Ā ┬Ā is the vector that coincides with the altitude directed from the vertex B the side AD, then┬Ā
┬Ā is the vector that coincides with the altitude directed from the vertex B the side AD, then┬Ā ┬Āis given byLet ABCD be a parallelogram such that AB = q,AD = p and ŌłĀBAD be an acute angle. If r is the vector that coincides with the altitude directed from the vertex B to the side AD, then r is given by (1)
┬Āis given byLet ABCD be a parallelogram such that AB = q,AD = p and ŌłĀBAD be an acute angle. If r is the vector that coincides with the altitude directed from the vertex B to the side AD, then r is given by (1)