 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsTwo sides of a rhombus are along the lines, x−y+1=0 and 7x−y−5=0. If its diagonals intersect at (−1, −2), then which one of the following is a vertex of this rhombus?
(−3, −9)
(−3, −8)
(1/3, -8/3)
(1/3, -8/3)
The centres of those circles which touch the circle, x2+y2−8x−8y−4=0, externally and also touch the x-axis, lie on:
a circle
an ellipse which is not a circle
a hyperbola.
a hyperbola.
If one of the diameters of the circle, given by the equation, x2+y2−4x+6y−12=0, is a chord of a circle S, whose centre is at (−3, 2), then the radius of S is:
5√2
5√3
5
10
Let P be the point on the parabola, y2=8x which is at a minimum distance from the centre C of the circle, x2+(y+6)2=1. Then the equation of the circle, passing through C and having its centre at P is:
x2+y2−4x+8y+12=0
x2+y2−x+4y−12=0
x2+y2− 4 x +2y−24=0
x2+y2− 4 x +2y−24=0
A.
x2+y2−4x+8y+12=0
Centre of circle x2 + (y+6)2 = 1 is C (0,6)
Let the coordinates of point P be (2t2, 4t)
Now, let 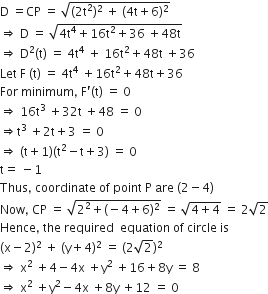
The eccentricity of the hyperbola whose length of the latus rectum is equal to 8 and the length of its conjugate axis is equal to half of the distance between its foci, is:
4/3
4/√3
2/√3
√3
The distance of the point (1, −5, 9) from the plane x−y+z=5 measured along the line x=y=z is:
3√10
10√3
10/√3
20/3
If the standard deviation of the numbers 2, 3, a and 11 is 3.5, then which of the following is true?
3a2−26a+55=0
3a2−32a+84=0
3a2−34a+91=0
3a2−34a+91=0
