A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification −1 on a screen placed at a distance of 50 cm from the mirror.
(a) Write the type of mirror.
(b) Find the distance of the image from the object.
(c) What is the focal length of the mirror?
(d) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
a) The image formed is real because magnification is negative. Therefore, the type of mirror used is a concave mirror.
b) 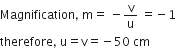
So, distance of the image from the object = |u| +|v| =100 cm
c) Using the mirror formula, we have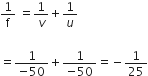
d) The given diagram shows the image formation.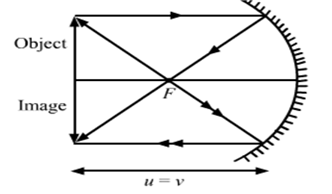
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray which is directed parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror. Mark on it the angle of incident and the angle of reflection.
The figure drawn below illustrates the path of reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray which is directed parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror. 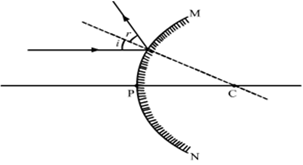
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm.
The two rays chosen for the construction of ray diagram is:
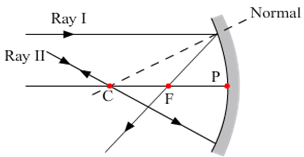
Ray 1: When the incident ray is parallel to the principal axis, the reflected ray will pass through the focus of concave mirror or it appears to pass through the focus of convex mirror.
Ray 2: When the incident ray passes through or appears to pass through the centre of curvature, the light, after reflection from the spherical mirror, reflects back along the same path.
The image formed is real, inverted, magnified and is formed beyond the centre of curvature.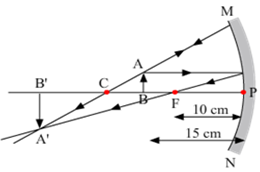
List four characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors.
Characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors are:
i) The image formed is of the same size as that of the object.
ii) Images are formed behind the mirrors and are at the same distance from the mirror as that of the object.
iii) The virtual and erect image is formed.
iv) The images are laterally inverted.
To find the image-distance for varying object-distances in case of a convex lens, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object placed very far from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image of the screen.
(a) In which direction – towards or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the object?
(b) What happens to the size of image – does it increase or decrease?
(c) What happen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
a) The position of the object moves away from the lens, as the student moves the object towards the lens. The screen should be moved away from the lens in order to obtain a sharp image.
b) When the object is moved near the lens, size of the image increases.
c) When the object is moved very close to the lens, it can be assumed to be placed between the focus and the optical centre. Then, the image formed is virtual, erect and enlarged.
