Diabetes mellitus : It is commonly called sugar disease. It is caused due to the lack of secretion of insulin.
Symptoms : The disease is characterised by the following:
1. Sugar in the urine.
2. Frequent urination.
3. Thirst increases.
5. Ketone bodies are formed and may be excreted with the urine.
6. Weakness.
7. Healing of the wound takes more time.
Pancreas : The pancreas is a is a exocrine as well as endocrine gland. The pancreas has two types of cells :
(a) Pancreatic gland cells : These cells secrete enzymes.
(b) Islets of Langerhans : These are the endocrine part of the pancreas. These cells are further of following types :
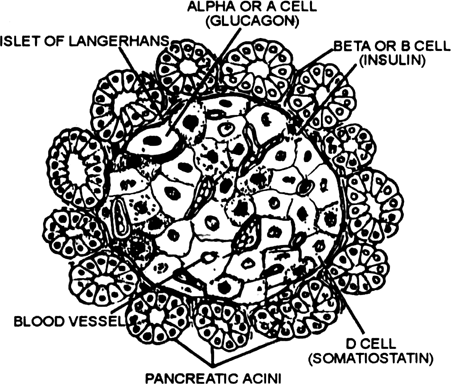
Fig. A part of the section of pancreas to show an islent of Langerhans.
(i) Alfa cells : These secrete glucagon. The glucagon converts glycogen into glucose. This process is called glycogenolysis.
(ii) Beta cells : These secrete insulin. It converts glucose to glycogen in liver. This process is called glycogenesis.
(iii) Delta cells : These secrete somatostanin hormone which controls the rate of absorption of food.
The hormones produced are:
1. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) : It is a proteinaceous hormone. It acts on the thyroid gland and regulates the secretion of the thyroid hormone.
2. Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH or Corticotropin hormone) : It is a peptide hormone. It controls functioning of adrenal cortex, especially secretion of glucocorticoids & sex corticoids.
3. Growth hormone, somatotropin hormone (STH) : It is a proteinaceous hormone. It regulates the synthesis of growth of the body.
4. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) : It is a glycoprotein gonadotrophic hormone. It controls spermatogenesis in testes, maturation of graafian follicles and secretion of estrogens in ovaries.
5. Luteinising hormone (LH) : It performs the following functions
(i) In females LH helps in growth and development of graafian follicles, ovulation, growth of ruptured follicle.
(ii) In females LH also helps in secretion of progestrone by corpus luteum.
(iii) IIn males it acts on Leydig’s or interstitial cells of testes to secrete testosterone and other androgens.
6. Prolactin (PRL) : It is a proteinaceous hormone. It stimulates development of mammary glands during pregnancy and lactation after child birth.
Ovaries : The ovaries secrete the following hormones :
(1) Estrogen : It is secreted by graafian follicles. Estrogen performs the following functions :
a. It brings ovulation.
b. It brings development of genital ducts.
(2) Progesterone : It is secreted by corpus luteum. The progesterone help in the implantation. The progesterone also maintains the enlargement of uterine wall during pregnancy.
(3) Relaxin : It is secreted by corpus luteum (part of graafian follicle after ovulation) at the end of gestation period. It enlarges the pelvic region during the childbirth.
