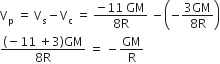From the tower of height H, a particle is thrown vertically upwards with a speed u. The time taken by the particle to hit the ground is n times that taken by it to reach the highest point of its path. The relation between H,u and n is
2gH = n2u2
gH = (n-2)2u2
2gH = nu2(n-2)2u2
2gH = nu2(n-2)2u2
C.
2gH = nu2(n-2)2u2
Time is taken to reach the maximum height t1 = u/g
If t2 is the time taken to hit the ground,
i.e, 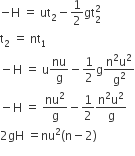
A uniform string of length 20 m is suspended from a rigid support. A short wave pulse is introduced at its lowest end. It starts moving up the string. The time taken to reach the support is: (take g = 10 ms−2 )

2s


C.

A uniform string of length 20 m is suspended from a rigid support. Such that the time taken to reach the support.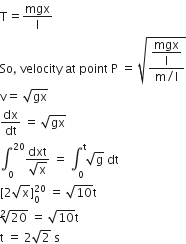
A satellite is revolving in a circular orbit at a height ‘h’ from the earth’s surface (radius of earth R ; h<<R). The minimum increase in its orbital velocity required, so that the satellite could escape from the earth’s gravitational field, is close to: (Neglect the effect of atmosphere.)




D.

Given, a satellite is revolving in a circular orbit at a height h from the Earth's surface having radius of earth R, i.e h <<R
Orbit velocity of a satellite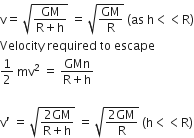
therefore, the minimum increase in its orbital velocity required to escape from the Earth's Gravitational Field.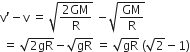
Two stones are thrown up simultaneously from the edge of a cliff 240 m high with an initial speed of 10 m/s and 40 m/s respectively. Which of the following graph best represents the time variation of relative position of the second stone with respect to the first? (Assume stones do not rebound after hitting the ground and neglect air resistance, take g = 10 m/s2 )
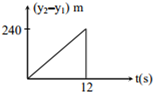
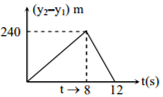
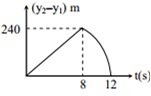
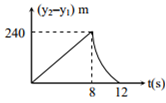
C.

The concept of relative motion can be applied to predict the nature of motion of one particle with respect to the other.
Consider the stones thrown up simultaneously as shown in the diagram below.
Considering the motion of the second particle with respect to the first we have relative acceleration
|a21| = |a2-a1| = g-g = 0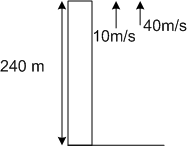
Thus, motion of the first particle is straight line with respect to the second particle till the first particle strikes ground at a time given by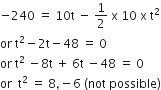
Thus, distance covered by the second particle with respect to the first particle in 8s is
S12 = (v21) t = (40-10)(8s)
= 30 x 8 = 240m
Similarly, time taken by the second particle to strike the ground is given by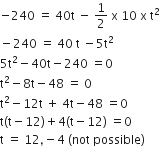
Thus, after the 8s magnitude of relative velocity will increases up to 12 s when the second particle strikes the ground.
From a solid sphere of mass M and radius R, a spherical portion of radius R/2 is removed, as shown in the figure. Taking gravitational potential V = 0 at r = ∞, the potential at the centre of the cavity thus formed is (G = gravitational constant)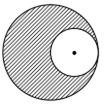
-GM/2R
-GM/R
-2GM/3R
-2GM/R
B.
-GM/R
Consider cavity as negative mass and apply superposition of gravitational potential.
Consider the cavity formed in a solid sphere as shown in figure
V (∞) = 0
According to the question, we can write potential at an internal point P due to the complete solid sphere.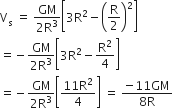
Mass of removed part,
=![]()
Potential at point P due to removed part![]()
Thus, potential due to remaining part at point P,