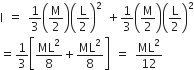The ratio of the radii of gyration of a circular disc to that of a circular ring, each of same mass and radius, around their respective axes is

B.
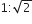
The square root of the ratio of the moment of inertia of rigid body nad its mass is called radius of gyration.
As in key idea, radius of gyration is given by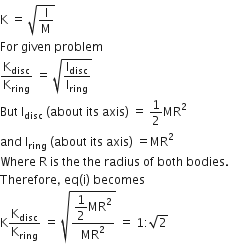
A thin conducting ring and radius R is given charge +Q. The electric field at the centre O of the ring due to the charge on the part AKB of the ring is E. The electric field at the centre due to the charge on the part ACDB of the ring is
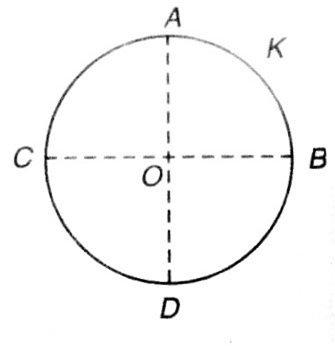
3E along KO
E along OK
E along KO
E along KO
B.
E along OK
A Wheel has an angular acceleration of 3.0 rad/s2 and an initial angular speed of 2.00 rad/s. In a time of 2s it has rotated thorough an angle (in radian) of:
6
10
12
12
B.
10
Angular acceleration is time derivative of angular speed and angular speed is time derivative of angular displacement.
By definition,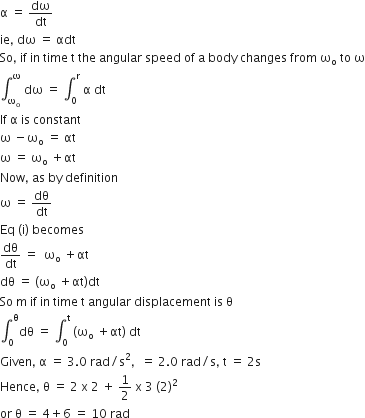
A bar magnet having a magnetic moment of 2 x 104 JT-1 is free to rotate in a horizontal plane. A horizontal magnetic field B = 6 x 10-4 T exists in the space. The work is done in taking the magnet slowly from a direction parallel to the field to a direction 60o from the field is
0.6 J
12 J
6 J
6 J
C.
6 J
The work done in rotating a magnetic dipole against the torque acting on it, when placed in a magnetic field is stored inside it in the form of potential energy.
When magnetic dipole is rotated from initial position θ = θ1 to final position θ = θ2, then work done = MB (cos θ1 = cos θ2)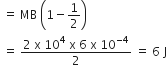
A thin rod of length L and Mass M is bent at its midpoint into two halves so that the angle between them is 90o. The moment of inertia of the bent rod about an axis passing through the bending point and perpendicular to the plane defined by the two halves of the rod is
ML2/24
ML2/12
ML2/6
ML2/6
B.
ML2/12
Since rod is bent at the middle, so each part of it will have same length (L/2) and mass (M/2) as shown,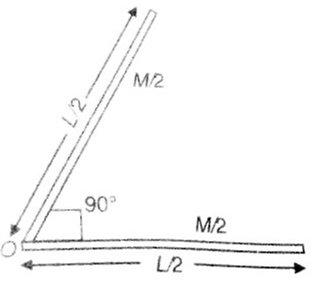
Moment of inertia of each part through its one end
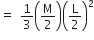
Hence, net moment of inertia through its middle point O is