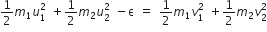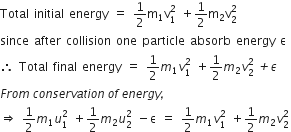Two similar springs P and Q have spring constants KP and KQ, such that KP>KQ. They are stretched, first by the same amount (case a), then by the same force (case b). The work done by the springs WP and WQ are related as, in case (a) and case (b), respectively
WP =WQ ;WP> WQ
WP =WQ ;WP= WQ
WP > WQ ;WQ> WP
WP > WQ ;WQ> WP
C.
WP > WQ ;WQ> WP
Given KP>KQ
In case (a) the elongation is same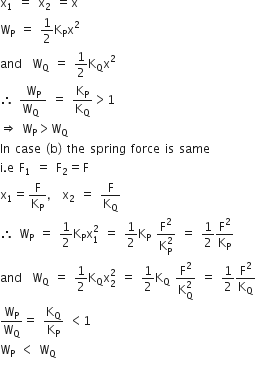
A block of mass 10 kg, moving in the x-direction with a constant speed of 10 ms-1 , is subjected to a retarding force F= 0.1x J/m during its travel from x = 20 m to 30 m. Its final KE will be
475 J
450 J
275 J
275 J
A.
475 J
From work energy theorem
work done = change in KE
⇒ W = Kf -Ki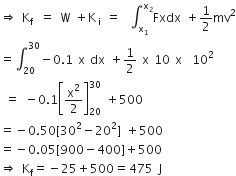
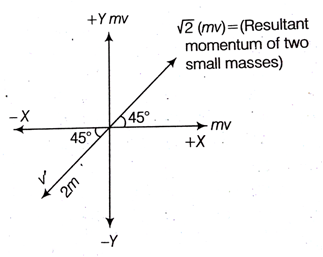
A body of mass (4m) is lying in x-y plane at rest. It suddenly explodes into three pieces. Two pieces each of mass m move perpendicular to each other with equal speed (v). The total kinetic energy generated due to explosion is,
mv2
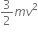
2mv2
2mv2
B.
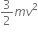
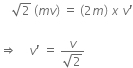
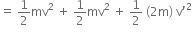
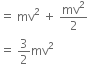
A car of mass m starts from rest and accelerates so that the instantaneous power delivered to the car has a constant magnitude Po. The instantaneous velocity of this car is proportional to
t2Po
t1/2
t-1/2
t-1/2
B.
t1/2
Power Po = Fv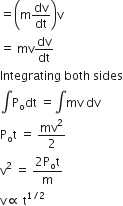
Two particles of masses m1,m2 move with initial velocities u1 and u2. On collision, one of the particles gets excited to a higher level, after absorbing energy (E). If final velocities of particles be v1 and v2, then we must have

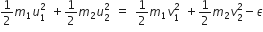
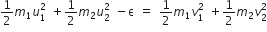
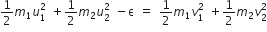
C.