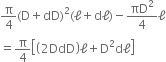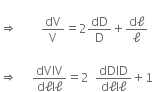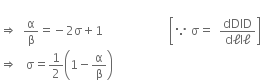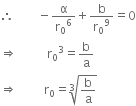
The stress-strain graphs for materials A and B are as shown in figure. Which of the material:
(i) has greater value of Young's modulus,
(ii) is more ductile or more brittle? 
(i) For graph A, slope of OE is more than that of graph B. Therefore, Young's modulus of material A is greater than that of B.
(ii) Material A shows wider plastic region than that of B. Thus, A is ductile than B and B is more brittle than A.
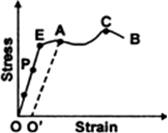
(a) Upto what point on the curve is the Hooke’s law obeyed? (This point is sometimes called ‘Proportional limit’).
(b) Which point on the curve corresponds to ‘elastic limit’ or yield point of the wire?
(c) Indicate the elastic and plastic regions of the stress-strain graph.
(d) Describe what happens when the wire is loaded upto a stress corresponding to the point A on the graph, and then unloaded gradually. In particular, explain the dotted curve.
(e) What is peculiar(odd) about the portion of the stress-strain graph from C to B? Upto what stress can the wire be subjected without causing fracture?
(a) Hooke's law states that that stress is directly proportional to strain. From the graph, we can say that Hooke’s law is obeyed from point O to P.
(b) E point on the curve corresponds to elastic limit or the yield point.
(c) Elastic region is the region in which the body regains its state after removal of stress and is from O to E. Plastic region is the region in which there is residue strain after removing the stress and that region is E to B.
(d) From O to P, the strain is directly proportional to stress, beyond P increase in strain is more for same increase in stress. Beyond E, when stress is increased, it does not retrace its path on decreasing the stress, but returns to point O' along path AO'. Therefore there is residue strain of 00' when stress is increased corresponding to the point A.
(e) From C to B, strain increases even if the wire is being unloaded and at B, it fractures. Till point C, stress can be applied without causing the fracture.
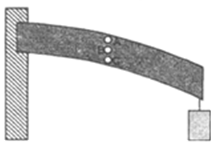
At point A, the beam undergoes tensile strain, therefore hole at A will increase in size along the length of the beam and becomes oblate.
At point C, the beam undergoes compression strain, therefore hole at C will decrease in size along the length of beam and becomes prolate.
The point B is in neutral zone, therefore the hole at B will be circular.
Let a wire of length l, diameter d be loaded by force F.
Let dl be the change in length and dV the change in volume, and dD be the change in the diameter.
Volume of wire before the force is applied is,
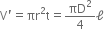
Volume of wire after the force is applied is,

Change in volume is,
dV = V' - V