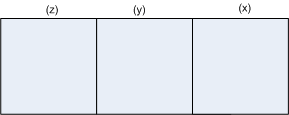
Event 1: A coin is tossed and the outcomes recorded.
Number of outcomes ![]()
![]() m = 2
m = 2
Event 2: The coin is tossed again and the outcomes recorded.
Number of outcomes ![]()
![]() n = 2
n = 2
Event 3: The coin is tossed third time and the outcomes recorded.
Number of outcomes ![]()
![]() p = 2
p = 2
∴ By fundamental principle of counting, the total number of outcomes recorded
= ![]()
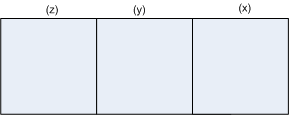
How many 3-digit numbers can be formed from the digits 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 assuming that repetition of the digits is not allowed.
Number of ways in which place (x) can be filled = 5
m = 5
Number of ways in which place (y) can be filled = 4 (∵ Repetition is not allowed)
n = 4
Number of ways in which place (z) can be filled = 3 (∵ Repetition is not allowed)
p = 3
∴ By fundamental principle of counting, the total number of 3 digit numbers formed
= m x n x p = 5 x 4 x 3 = 60.
How many 3-digit numbers can be formed from the digits 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 assuming that repetition of the digits is allowed.