
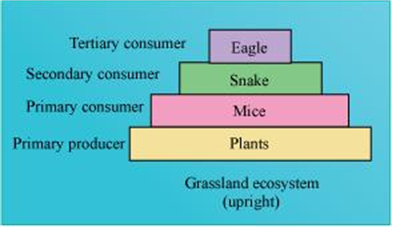
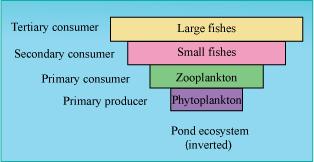
Define ecological pyramids and describe with examples, pyramids of number and biomass.
It is expressed in terms of gm-2yr-1 or kcal m-2 yr-1. Primary productivity depends upon a number of environmental factors like :
(a) Availability of nutrients which varies in different types of ecosystem.
(b) Photosynthetic capacity of plants.
(c) The plant species inhabiting a particular area.
(d) Environmental factors.
An ecosystem comprises two main components :
(i) Biotic components including plants, animals and microorganisms : and
(ii) Abiotic components that mainly includes non-living factors like water, minerals, temperature and light.
B.
50%Decomposition involves the following processes :
1. Fragmentation - is the breaking down of the detritus into smaller particles . It increases the surface area of detritus for the action of microbes.
2. Leaching is the downward movement of water soluble inorganic nutrients into the soil horizon and their precipitation as unavailable salts.
3.Catabolism involves break down of detritus in the presence of extracellular enzymes released by the decomposers.
Usually the processes fragmentation , leaching and catabolism are carried out simultaneously on the detritus.
4.Humification involves transformation of simplified detritus into fully decomposed, dark coloured and amorphous humus. Humus acts as a reservoir of nutrients.
5. Mineralisation is the further breakdown of the humus by microbes to relase inorganic nutrients.
