(ii)Cooperative security may also involve a variety of other players, both national and International Organisations – the UN, World Health Organisation, the World Bank and other institutions – also play a significant role in cooperative security.
(iii) Non-governmental Organisations – Amnesty International, the Red Cross etc. play an important role in it. Great personalities like Mother Teresa, Nelson Mandela are also involved in it.
(iv) The international community have to sanction the use of force is used as a last resort to deal with governments that kill their own people or ignore the miseries of their poor population who are devastated by poverty, disease and catastrophe.
(i) India’s first component is the strengthening of military capabilities. India has been involved in conflicts with its neighbours–Pakistan in 1947-48,1965,1971 and 1999; and China in 1962. India is surrounded by nuclear armed countries in the South Asian region.
(ii) The second component of India’s security has been to strengthen international norms and international institutions to protect its security interests.
(iii) The third component has been to preserve national unity by adopting a democratic political system which allows different communities and groups of people to freely articulate their grievances and share political power.
(iv) The fourth component of India’s security has been to develop its economy in a way that vast mass of citizens are lifted out of poverty and misery and huge economics qualities are not allowed to exist.
(ii) Proponent of the ‘narrow’ concept of human security focus on violent threats to individual.
(iii)While the ‘broad’ concept of human security includes threats from hunger, disease and natural disasters which kill more people than war, genocide and terrorism combined.
(iv)It has also emphasised on economic security and ‘threats’ to human dignity i.e., ‘freedom from want’ and ‘freedom from fear’.
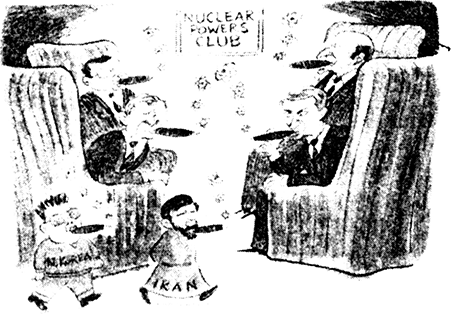
(i) How do the big powers react when new countries claim nuclear status ?
(ii) On what basis can we say that some countries can be trusted with nuclear weapons while others can’t be ?
(ii) Countries with nuclear weapons can be trusted if it declares usage of nuclear energy for peaceful purposes, while the countries which builds nuclear arsenal can not be trusted.
