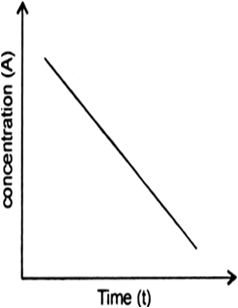
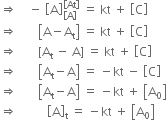Nitric oxide reacts with hydrogen to give nitrogen and water:
The kinetic of this reaction is explained by the following steps:
(i) 2NO + H2 → N2 + H2O2 (slow)
(ii) H2O2+ H2 → 2H2O (fast)
What is the predicted law?
2 NO + 2H2 → N2 + 2H2O
The reaction involves 4 molecules but it has been found to be of third because it takes place in the following steps:
(i) 2NO + H2 → N2 + H2O2 (slow)
(ii) H2O2 + H2 → 2H2O (fast)
Step (i) being slow, is rate determining step.
The rate is given by
222 Views