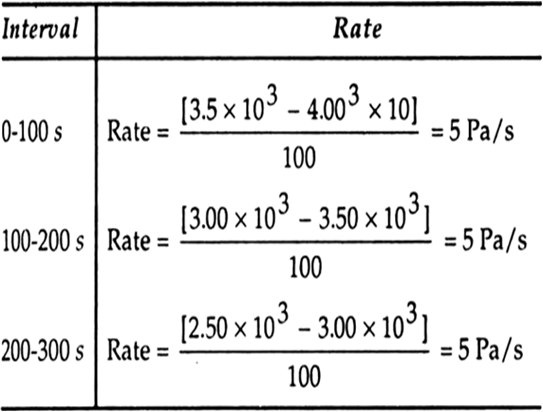
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) reacts with fluorine (F2) to form nitryl fluoride (NOzF) according to the reaction
(i) Rate of formation of
(ii) Rate of disappearance of
(iii) Rate of disappearance of
|
t/s |
0 |
100 |
200 |
300 |
|
p/pascal |
4.0 x 103 |
3.5 x 103 |
3.0 x 103 |
|