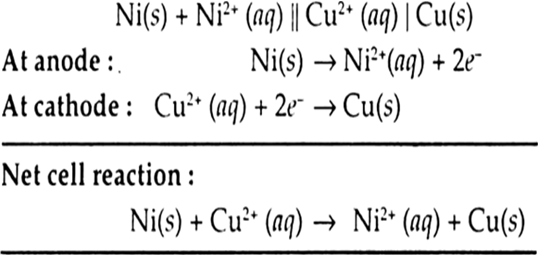Define molar conductivity of an electrolytic solution. Mention the effect of temperature on molar conductivity.
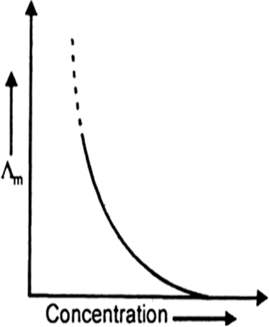
Molar conductivity is defined as the electrolytic conductivity power of all the ions furnished by 1 mol of the electrolyte at a given concentration in solution. It is given as
where Am = Molar conductivity.
k = Specific conductivity. Cm = Concentration in molar per litre.
Effect of temperature on molar conductivity. The speed of movement of ions increases with an increase in temperature. Therefore, molar conductivity increases with temperature.
235 Views