The concentration of all species involved in the species involved in the electrode reaction is unity.This need not be always true.
Nernst shows that for the electrode reaction:
the electrode potential at any concentration measured with respect to standard hydrogen electrode can be represented by:
but concentration of solid M is taken as unity as we have
R is gas constant (8.314 JK–1 mol–1),
F is Faraday constant (96487 C mol–1), T is temperature in kelvin and [Mn+] is the concentration of the species.
In Daniell cell, the electrode potential for any given concentration of
Cu2+ and Zn2+ ions, we write
For cathode:-
The cells from which electric energy is derived by irreversible chemical action are called primary cells. The primary cell is capable of providing an EMF when its constituent’s two electrodes and a suitable electrolyte are assembled together. The three main primary cells namely are the Daniel cell, the Leclanche cell, and the dry cell. None of these cells can be recharged electrically.
The dry cell consists of a zinc container that also acts as anode and the cathode is a carbon (graphite) rod surrounded by powdered manganese dioxide and carbon. The space between the electrodes is filled by a moist paste of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) and zinc chloride (ZnCl2). The electrode reactions are complex, but they can be written approximately as follows :
Anode: Zn(s)----> Zn2+ + 2e–
Cathode: MnO2+ NH4+ + e–----> MnO(OH) + NH3
In the reaction at cathode, manganese is reduced from the + 4 oxidation state to the +3 state. Ammonia produced in the reaction forms a complex with Zn2+ to give [Zn (NH3)4]2+. The cell has a potential of nearly 1.5 V.
Strong electrolytes: The molar conductivity of a strong electrolyte decreases slightly with the increase in concentration. This decrease is due to the increase in interionic attractions as a result of greater numbr of ions per unit volume. With dilution, the ions are far apart, inter ionic attractions become weaker and conductance increases.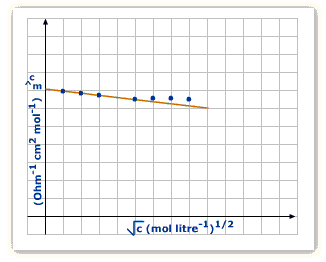
Electrolysis of molten NaCl gives sodium at cathode while aqueous NaCl gives H2 gas at cathode.
Molten NaCl dissociates to give Na+ and Cl-, Na+ then move towards cathode, picks up one electron and gets reduced to form Na.
Na+ +e- ---> Na
In aqueous NaCl, as , it is the hydrogen gas which liberates at cathode.
