conductivity and molar conductivity change with the concentration of the electrolyte. Conductivity always decreases with decrease in concentration both, for weak and strong electrolytes.
Molar conductivity varies with the concentration of electolytes.
Here b = Experimental constant
Λ∞m = Molar conductivity at infinite solution.
The plot of Λ∞m versus would give a straight line.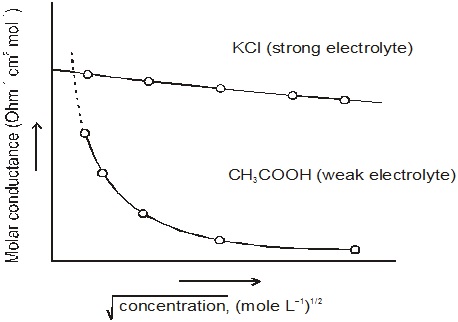
Corrosion slowly coats the surfaces of metallic objects with oxides or other salts of the metal. The rusting of iron, tarnishing of silver, development of green coating on copper and bronze are some of the
examples of corrosion.
Salt bridge. A salt bridge consists of a saturated solution of NH4NO3 or KCl mixed with gelatin or agar jelly filled in a glass tube bent according to the requirement of the experiment.
Significance:
(i) Salt bridge prevents mixing of two electrolytes.
(ii) Prevents junction potential.
(iii) Maintains electrical neutraility.
Zinc is more electro-positive than iron. Therefore, as long as zinc is there on the iron pipe, zinc acts as anode and the iron as cathode. As a result, rusting of iron is prevented.
On the other hand, tin is less electro-positive than iron. Therefore, when tin coating over iron gets broken, iron acts as anode and gets oxidised. Thus even when tin is there, the exposed iron gets rusted.
