
Explain the basis of similarities and differences between metallic and ionic crystals.
|
Characteristics |
Ionic crystals |
Metallic crystals |
|
|
1. |
Constituent particles |
cations (positive ions) and anions (negative ions) |
Positive ions and mobile electrons. |
|
2. |
Binding forces |
Strong electrostatic forces (electro valent bonding) |
Electrical attraction between positive ions and mobile electrons (metallic bonding) |
|
3. |
Physical properties |
Hard and brittle; high m.p. and b.p. good conductors of heat and electricity in molten state and aqueous solution, high heat of fusion. |
Hard but malleable, high m.p., very good conductors of heat and electricity in solid and molten state, moderate heats of fusion. |
The solids which have intermediate conductivities generally between 10–6 to 104 m–1are called semi-conductors. For example, germanium and silicon. The two main types of semi-conductors are as follows:
(i) n-type semi-conductor : When a silicon crystal is doped with atoms of group-15 elements, such as P, As, Sb or Bi, then only four of the five valence electrons of each impure atom participate in forming covalent bonds and fifth electron is almost free to conduct electricity. Silicon that has been doped with a group-15 element is called n-type semi-conductor.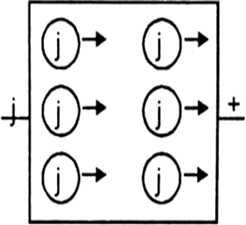
n-type semi-conductor.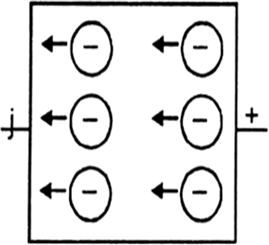
p-type semi-conductor.
ii) p-type semi-conductor: When a silicon crystal is doped with atoms of group B elements, such as B, Al, Ca or In, each impurity atom forms only three covalent bonds with the host atoms. The place where the fourth electron is missing is called a hole which moves through the crystal like a positive charge and hence increases its conductivity. Silicon that has been doped with group-B element is called p-type semi-conductor.
Explain Ionic solids are hard and brittle.
Solution:
(i) One unit cell of a face-centered cubic has 8 lattice points are corners and 6 lattice points at faces, total 14 lattice points.
(ii) One unit cell of face-centered tetragonal has 8 lattice points are corners and 6 lattice points at faces, total 14 lattice points.
(iii) One unit cell of body centered has 8 lattice points are corners and 1 lattice points at faces, total 9 lattice points.
