
(i) Ge is an element of 14th group (like Si) and has configuration 4s24p2. It has been doped with In, a 13th group element having 5s25p1 configuration i.e., element of 14th group has been doped with 13th group element. All three valence electrons of impurity atom (In) gets bonded with three out of four eectrons of Ge and one electron of Ge remains unbonded. Conductivity is due to unbonded electron of insulator, Ge. Therefore, it is a p-type semi-conductor.
(ii) Boron, B is an element of 13th group and has 2s22p1 configuration. It is doped with Si, an element of 14th group having 3s23p2 configuration. All three electrons of boron gets bonded with 3 out of 4 electrons of Si and 4th electron of impurity atom (i.e., Si) is responsible for conductivity. Thus it is a n-type semiconductor.
Let us Suppose the number of oxide (O2–) ions = N.
Number of octahedral void = number of anions
So that the number of octahedral voids = N
We have Given that
Two out of every three octahedral holes are occupied by ferric ions.
So that the number of ferric (Fe3+) ions = 2N/3
The ratio of the number of Fe3+ ions to the number of O2− ions,
Fe3+ : O2− = 2N/3 : N
Multiply 3 and divide by N we get
Fe3+ : O2− = 2 : 3
Hence, the formula of the ferric oxide is Fe2O3.
In the sample of cuprous oxide, Cu2O prepared in laboratory, copper to oxygen ratio is less than 2 : 1 and this deficiency of copper causes the metal deficiency defects. In these defects the positive ions are less in number as compared to anions. These defects are caused in two ways:
(i) By Cation Vacancies : Some Cu+ may be missing from lattice sites and their positive charges are balanced by presence of extra charge on adjacent cations i.e., some Cu2+ are present and some cation vacancies are present.
(ii) By presence of extra anions at interstitial sites: The type of defect can arise where some oxide ion, O2– are present at lattice sites and their charge is balanced by neighbouring cations in higher oxidation states i.e., some Cu2+ ions are present instead of Cu2+ ions.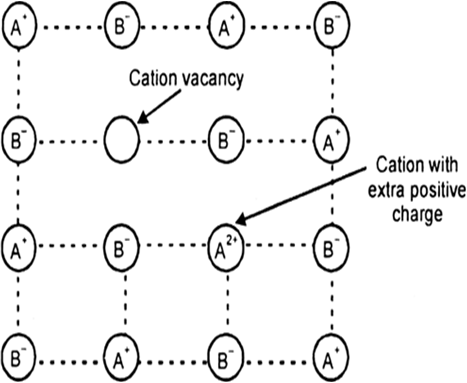
Metal deficiency defect due cation vacancy.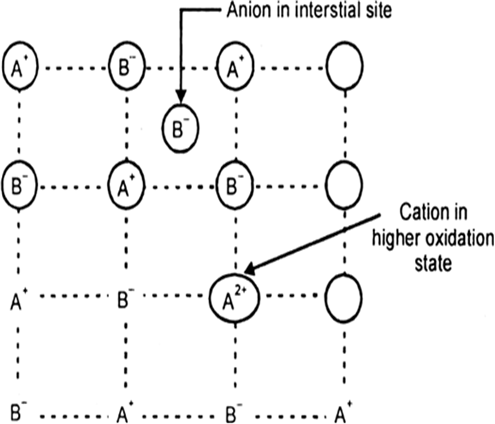
Metal deficiency defect due to presence of extra anions.
