
We have given that
Length of edge, a = 3.61x10–8 cm
Atomic mass of cupper, M = 63.55 g/mol
Avogadro constant, NA = 6.022x1023 per mol
Number of atoms in unit cell of FCC, Z= 4
Use formula of density,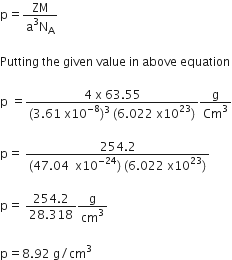
(i) Simple Cubic: A simple cubic unit cell has one sphere (or atom) per unit cell. If r is the radius of the sphere, then volume occupied by one sphere present in unit cell = ![]()
Edge length of unit cell (a) = r + r = 2r
Volume of cubic ![]()
Volume of occupied by sphere = ![]()
Percentage volume occupied = percentage of efficiency of packing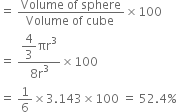
For simple cubic metal crystal the efficiency of packing = 52.4%.
(b) Body centred cubic: From the figure it is clear that the atom at the centre will be in touch with other two atoms diagonally arranged and shown with solid boundaries.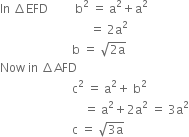
The length of the body diagonal c is equal to 4r where r is the radius of the sphere (atom). But c = 4r, as all the three spheres along the diagonal touch each other
∴ ![]()
or ![]()
or ![]()
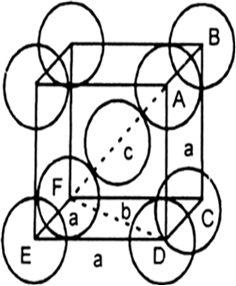
Fig. BCC unit cell. In this sort of structure total number of atoms is two and their volume is ![]()
Volume of the cube, a3 will be equal to![]()
Therefore, Percentage of efficiency Volume occupied by four - spheres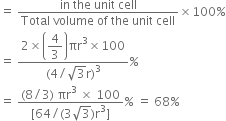
(c) Face centred cubic: A face centred cubic cell (fcc) contains four spheres (or atoms) per unit volume occupied by one sphere of radius
r = 4/3 ![]() r3
r3
Volume occupied by four spheres present in the unit cell
r = 4/3 ![]() r3 x 4 = 16/3
r3 x 4 = 16/3 ![]() r3
r3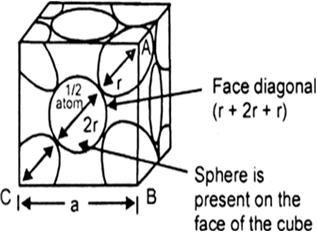
Fig. Face centred cubic unit cell. Figure indicates that spheres placed at the corners touches a face centred sphere. Length of the face diagonal
= r + 2r + r = 4r
Hence, for face centred cubic, efficiency of packing = 74%.
In terms of band theory, what is the difference between a conductor and an insulator?
Solution:
Molecular orbirals of metals are formed by atomic orbitals. These orbitals are so close to each other as they form band or valence band.
(i) Difference between conductor and insulator - In conductors there is no energy gap between the valence band, which facilitates the flow of electrons easily under an applied electric field and metals show conductivity.
While in insulators there is large energy gap between the valence band and electrons cannot jump to it i.e. large energy gap prevents the flow of electricity.
(ii)Difference between conductors and semiconductor - In conductors there is no energy gap between the valence band and conduction band, which facilitates the flow of electrons easily under an applied electric field and metals show conductivity.
While in semi conductors, there is small energy gap between valence bond and conduction band. The small gap between band facilitates some electrons to jump to the conduction band by acquiring extra energy.
Formula is Ni0.98O1.00
So the ration of Ni : O = 98:100
So if there are 100 atoms of oxygen then 98 atoms of Ni,
Let number of atoms of Ni+2 = x
Then number of atoms of Ni+3 = 98–x
Charge on Ni = charge on O
So that oxygen has charge –2
3(98–x) + 2x = 2 (100)
294 –3x +2x = 200
–x = – 94
x = 94
Percentage of Ni+2 = (atom of Ni+2/total number of atoms of Ni)100
=100(94/98)x100
= 96%
Percentage of Ni+3
=100 – Ni+2
=100 – 96
= 4 %
