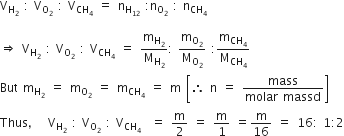Equal moles of hydrogen and oxygen gases are placed in a container with a pin-hole through which both can escape. What fraction of the oxygen escapes in the time required for one-half of the hydrogen to escape?
1/4
3/8
1/2
1/2
D.
1/2
we have given,
a number of moles of hydrogen and not equal.
not equal.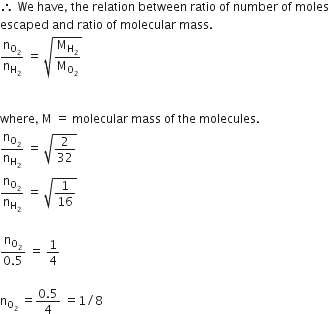
Liquid ‘M’ and liquid ‘N’ form an ideal solution. The vapour pressures of pure liquids ‘M’ and ‘N’ are 450 and 700mm Hg, respectively, at the same temperature. Then correct statement is:
(xM = Mole fraction of 'M' is solution; xN = Mole fraction of 'N' in solution; yM = Mole fraction of 'M' in vapour phase; yN = Mole fraction of 'N' in vapour phase)
(xM - yM) < (xN - yN)
C.
PM° = 450
1.0 g of magnesium is burnt with 0.56 g of O2 in a closed vessel. Which reactant is left in excess and how much?
Mg, 0.16 g
O2, 0.16 g
Mg, 0.44 g
Mg, 0.44 g
A.
Mg, 0.16 g
The balanced chemical equation is
Mg + 1/2O2 --> MgO
24g 16 g 40g
From the above equation, it is clear that,
24 f Mg reacts with 16 g O2
thus, 1.0 g Mg reacts with 
When 22.4 L of H2 (g) is mixed with 11.2 L of Cl2 (g), each of at STP, the moles of HCl (g) formed is equal to
1 mole of HCl (g)
2 moles of HCl (g)
0.5 mole of (g)
0.5 mole of (g)
A.
1 mole of HCl (g)
The given problem is related to the concept of the stoichiometry of chemical equations. Thus, we have to convert the given volumes into their moles and then identify the limiting reagent [possessing minimum number of moles and completely used up in the reaction]
The limiting reagent gives the moles of product formed in the reaction.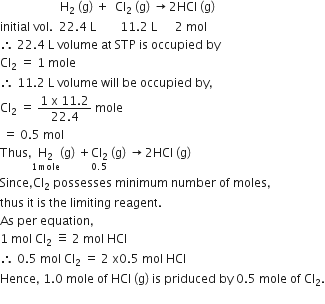
Equal masses of H2, O2 and methane have been taken in a container of volume V at temperature 270 C in identical conditions. The ratio of the volumes of gases H2 : O2: CH4 would be
8:16:1
16:8:1
16:1:2
16:1:2
C.
16:1:2
According to Avogadro's hypothesis,
Volume of a gas (V)  number of moles (n)
number of moles (n)
Therefore, the ratio of the volumes of gases can be determined in terms of their moles. The ratio of volumes of H2:O2: methane (CH4) is given by