 Short Answer Type
Short Answer TypeA consumer consumes only two goods X and Y. State and explain the conditions of consumer's equilibrium with the help of utility analysis.
In case of two commodities, the consumer’s equilibrium is attained in accordance with the Law of Equi-Marginal Utility. It states that a consumer allocates his expenditure on two goods in such a manner that the utility derived from each additional unit of the rupee spent on each of the commodities is equal.
i.e. Marginal utility of a rupee spent on commodity x = Marginal Utility of a rupee spent on commodity Y = Marginal Utility of Money.
Or
MUx/Px=MUy/Py = MUm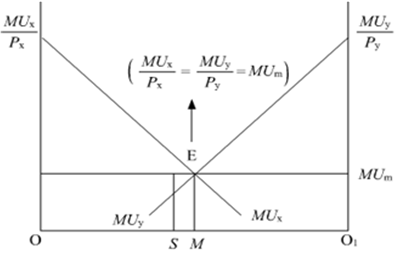
In the diagram, OO1 represents the total income of a consumer. Mux and MUy represents the Marginal Utility curves of commodity X and commodity Y, respectively. Equillibrium is established at point E, where, Mux and MUy intersect each other and with MUy.
At this point, OM amount of income is spent on commodity X and the remaining amount of income MO1 is spent on commodity Y.
Explain how the demand for a good is affected by the prices of its related goods. Give examples.
Define 'Market-supply'. What is the effect on the supply of a good when Government imposes a tax on the production of that good? Explain.
What is a supply schedule? What is the effect on the supply of a good when Government gives a subsidy on the production of that good? Explain.
 Long Answer Type
Long Answer TypeWhat is meant by producer's equilibrium? Explain the conditions of producer's equilibrium through the 'total revenue and total cost' approach. Use diagram.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is an 'increase' in demand for this good. Explain the chain of effects of this change. Use diagram.
 Short Answer Type
Short Answer Type