 Long Answer Type
Long Answer Type(a) Explain, giving reasons, the basic difference in converting a galvanometer into (i) a voltmeter and (ii) an ammeter.
(b) Two long straight parallel conductors carrying steady current I1 and I2 are separated by a distance ‘d’. Explain briefly, with the help of a suitable diagram, how the magnetic field due to one conductor acts on the other. Hence deduce the expression for the force acting between the conductors. Mention the nature of this force.a)
Conversion of galvanometer into ammeter: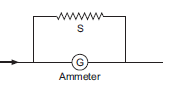
A galvanometer may be converted into ammeter by using very small resistance in parallel with the galvanometer coil.
The small resistance connected in parallel is called a shunt. If G is resistance of galvanometer, Ig is current in galvanometer for full-scale deflection, then for conversion of galvanometer into ammeter of range I ampere, the shunt is given by,![]()
Conversion of galvanometer into voltmeter,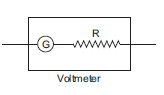
A galvanometer may be converted into voltmeter by connecting high resistance (R) in series with the coil of galvanometer.
If V volt is the range of voltmeter formed, then series resistance becomes,![]()
b)
Magnetic field produced by current I1 at any point on conductor Rs is given by, ![]()

Force acting on length l of the conductor RS will be,![]()
An equal force is exerted into the wire PQ by the field of conductor RS which is given by, ![]()
Thus, the force is attractive when the current is acting along the same direction.
When, current flows in opposite direction, the forces between the two conductors are repulsive.
a) In Young’s double slit experiment, derive the condition for (i) constructive interference and
(ii) Destructive interference at a point on the screen.
(b) A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths, 800 nm and 600 nm is used to obtain the interference fringes in a Young’s double slit experiment on a screen placed 1.4 m away. If the two slits are separated by 0.28 mm, calculate the least distance from the central bright maximum where the bright fringes of the two wavelengths coincide.
(a) How does an unpolarized light incident on a Polaroid get polarized?
Describe briefly, with the help of a necessary diagram, the polarization of light by reflection from a transparent medium.
(b) Two Polaroid’s ‘A’ and ‘B’ are kept in crossed position. How should a third Polaroid ‘C’ be placed between them so that the intensity of polarized light transmitted by Polaroid B reduces to 1/8th of the intensity of unpolarized light incident on A?(a) Describe briefly, with the help of a diagram, the role of the two important processes involved in the formation of a p-n junction.
(b) Name the device which is used as a voltage-regulator. Draw the necessary circuit diagram and explain its working.
OR
(a) Explain briefly the principle on which a transistor-amplifier works as an oscillator. Draw the necessary circuit diagram and explain its working.
(b) Identify the equivalent gate for the following circuit and write its truth table.
