 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsConsider an ideal gas confined in an isolated closed chamber. As the gas undergoes an adiabatic expansion the average time of collision between molecules increases as Vq , where V is the volume of the gas. The value of q is: 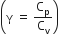
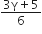
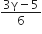
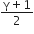
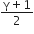
C.
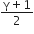
For an adiabatic process TVγ-1 = constant
We know that average time of collision between molecules
Thus, we can write
n =K1V-1 and Vrms = K2T1/2
Where K1 and K2 are constants.
For adiabatic process TVγ-1 = constant. Thus we can write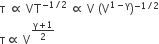
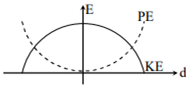
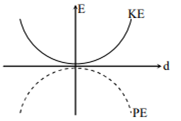
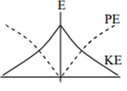
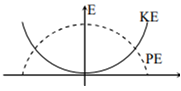
For a simple pendulum, a graph is plotted between its kinetic energy (KE) and potential energy (PE) against its displacement d. Which one of the following represents these correctly?
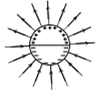
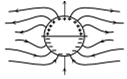
A long cylindrical shell carries positive surface charge in the upper half and negative surface charge in the lower half. The electric field lines around the cylinder will look like figure given in: (figures are schematic and not drawn to scale)


A uniformly charged solid sphere of radius R has potential V0 (measured with respect to ∞) on its surface. For this sphere, the equipotential surfaces with potentials 3Vo/2, 5Vo/4, 3V/4 and Vo/4 have radius R1, R2,R3 and R4 respectively. Then
R1 = 0 and R2>(R4-R3)
R1≠0 and (R2-R1)>(R4-R3)
R1 = 0 and R2<(R4-R3)
R1 = 0 and R2<(R4-R3)
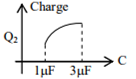
In the given circuit, charge Q2 on the 2 μF capacitor changes as C is varied from 1 μF to 3 μF. Q2 as a function of ‘C’ is given properly by : (figures are drawn schematically and are not to scale)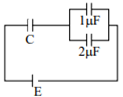
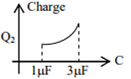
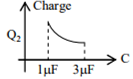
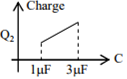
When 5V potential difference is applied across a wire of length 0.1 m, the drift speed of electrons is 2.5 × 10–4 ms–1. If the electron density in the wire is 8 × 1028 m–3, the resistivity of the material is close to:
1.6 x 10-8Ωm
1.6 x 10-7Ωm
1.6 x 10-6Ωm
1.6 x 10-6Ωm
In the circuit shown, the current in the 1Ω resistor is: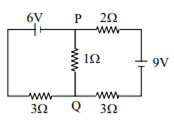
1.3 A from P to Q
0 A
0.13 A, from Q to P
0.13 A, from P to Q
Two coaxial solenoids of different radii carry current I in the same direction. Let 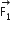 be the magnetic force on the inner solenoid due to the outer one and
be the magnetic force on the inner solenoid due to the outer one and 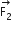 be the magnetic force on the outer solenoid due to the inner one. Then:
be the magnetic force on the outer solenoid due to the inner one. Then:
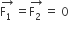
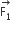 is radially inwards and
is radially inwards and 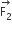 is radially outwards
is radially outwards
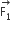 is radially inwards and
is radially inwards and 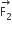 =0
=0
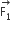 is radially inwards and
is radially inwards and 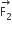 =0
=0
Two long current carrying thin wires, both with current I, are held by insulating threads of length L and are in equilibrium as shown in the figure, with threads making an angle ‘θ’ with the vertical. If wires have mass λ per unit length then the value of I is: (g = gravitational acceleration)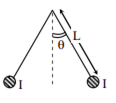



A rectangular loop of sides 10 cm and 5 cm carrying a current I of 12 A is placed in different orientations as shown in the figures below: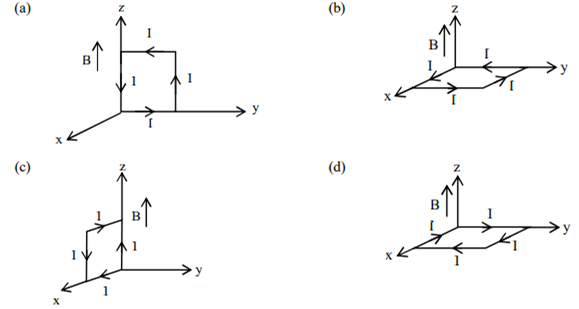
If there is a uniform magnetic field of 0.3 T in the positive z direction , in which orientations the loop would be in (i) stable equilibrium and (ii) unstable equilibrium?
(a) and (b) respectively
(a) and (c) respectively
(b) and (d) respectively
(b) and (d) respectively
