 Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice QuestionsIdentify the polysaccharide with -glycosidic bond
starch
glycogen
sucrose
cellulose
D.
cellulose
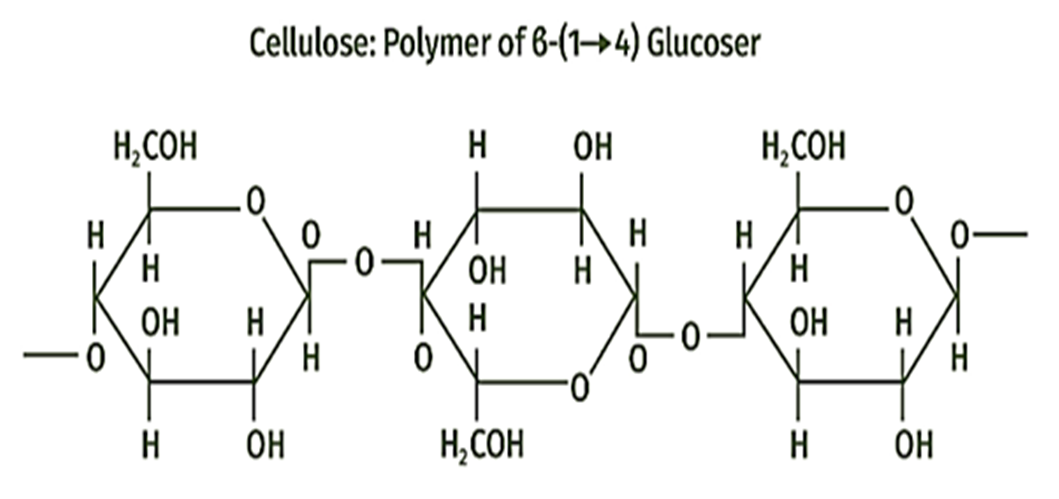
Cellulose is the most important structural component of the cell wall of plants. It is a linear polymer of -D glucose units connected through -1, 4 glycosidic linkage.
Simple storage protein that coagulates upon heating but remains soluble in dilute salt solution is correctly exemplified by
globulin
albumin
histone
collagen
N-acetyl muramic acid is found in
cell wall component of plant
cell wall component of Gram positive bacteria
cell wall component of fungi
viral coat material
Identify the bacterium that appears violet after Gram staining
Salmonella enterica
Escherichia coli
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Rhizobium meliloti
Portion of apical meristem that gives xylem tissue is called
protoxylem
procambium
metaxylem
tracheid
Higher animals cannot synthesize few fatty acids which are very essential for their growth and deveiopment. These fatty acids are typically
saturated
cyclic
unsaturated
branched
Identify the membrane across which the proton (H+) gradient facilitates ATP synthesis in a typical eukaryotic cell
plasma membrane
mitochondrial inner membrane
mitochondrial outer membrane
nuclear membrane
After forceful inspiration, the amount of air that can be breathed out by maximum forced expiration is equal to
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) + Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV) + Tidal Volume (TV) + Residual Volume (RV)
IRV + RV + ERV
IRV + TV + ERV
TV + RV + ERV
