Describing Motion
Rest: A body is said to be in a state of rest when its position does not change with respect to a reference point.
Motion : A body is said to be in a state of motion when its position change continuously with reference to a point.
Motion Along A Straight Line
Motion can be of different types depending upon the type of path by which the object is going through.
- Circulatory motion/Circular motion – In a circular path.
- Linear motion – In a straight line path.
- Oscillatory/Vibratory motion – To and fro path with respect to the origin.
Scalar quantity: It is the physical quantity having own magnitude but no direction e.g., distance, speed.
Vector quantity: It is the physical quantity that requires both magnitude and direction e.g., displacement, velocity.
Distance: The actual path or length travelled by an object during its journey from its initial position to its final position is called the distance.
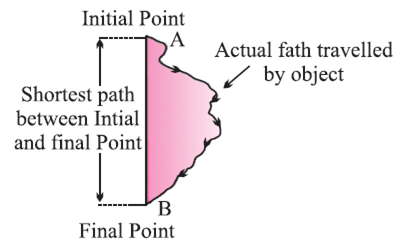
Displacement: It can be defined as the shortest distance between two points.
Difference between Distance and Displacement:
| Distance | Displacement |
| The total path travelled by the object | Shortest Distance travelled by the object |
| It is a scalar quantity | It is a vector quantity |
| It remains positive, can’t be ‘0’ or negative. | It can be positive (+ve), negative (-ve) or zero. |
Uniform Motion And Non Uniform Motion
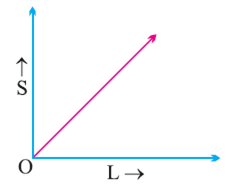
A body is said to have a uniform motion if it travels equal distances in equal intervals of time, no matter how small these intervals may be. For example, a vehicle running at a constant speed of 10m/ sec will cover equal distances of 10metres every second, so its motion will be uniform.
A body is said to have a non- uniform motion if it travels unequal distances in equal intervals of time, no matter how small these intervals may be. For example, a free ball from a certain height covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time, so its motion is non-uniform.
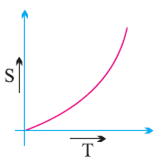
Non-uniform motion is of two types:
Accelerated Motion: When the motion of a body increases with time.
De-accelerated Motion: When the motion of a body decreases with time.