Advertisement
With the halp of ionic equations describe what happen: When
(i) pH of a solution of dichromate ions is raised.
(ii) Potassium manganate is electro-chemically oxidised.
when pH is increased, i.e., solution is more basic, orange coloured dichromate ion change to yellow coloured chromate ion.
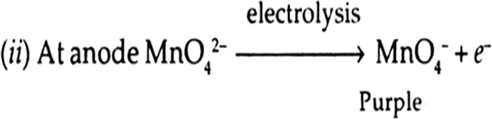
When potassium manganate is electro-chemically oxidised i.e., undergoes, electrolytic oxidation, it forms purple colour KMnO4.
266 Views
Advertisement
State two advantages of H2O fuel cell over ordinary cell.
The standard reduction potential values of three metal cations Xa+, Yb+ and Zc+are + 0.52, – 3.03, – 1.18 V respectively. Arrange the corresponding metals, in the order of their increasing reducing power.
Explain with the help of a diagram the effect of change in concentration of solution on the molar conductance of (i) a weak electrolyte, (ii) a strong electrolyte.
Explain why:
(i) E° for Mn3+ / Mn2+ couple is more positive than that Fe3+/Fe2+. (At. No. Mn = 25, Fe = 26).
(ii) Ce3+ can be easily oxidised to Ce4+ (At. No. Ce= 58).
(i) E° for Mn3+ / Mn2+ couple is more positive than that Fe3+/Fe2+. (At. No. Mn = 25, Fe = 26).
(ii) Ce3+ can be easily oxidised to Ce4+ (At. No. Ce= 58).
Advertisement