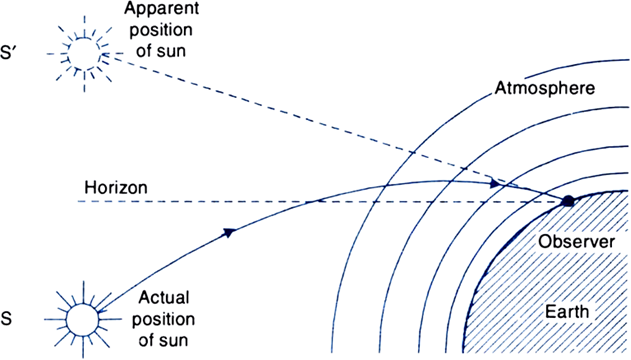
The interaction of sunlight with atmospheric particles gives rise to the following phenomena:
1. Blue colour of the sky.
2. Redishness of the sun at sunrise and sunset.
A beam of white light falling on a glass prism gets split up into seven colours marked 1 to 7 as shown in the diagram.
A student makes the following statements about the spectrum observed on the screen.
(a) The colours at positions marked 3 and 5 are similar to the colour of the sky and the core of a hard boiled egg respectively.
Is the above statement made by the student correct or incorrect? Justify.
(b) Which two positions correspond closely to the colour of (i) a solution of potassium permanganate?
(ii) ‘danger’ or stop signal lights? 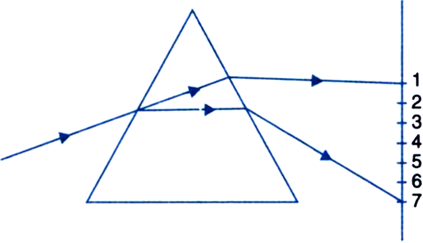
The colours of the spectrum observed on the screen are in the order:
|
V |
I |
G |
Y |
0 |
R |
|
7 |
6 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
(a) The statement made by the student is incorrect. He is stating the colours in the reverse order. Color at position 3 is yellow which is the color of a boiled egg and color at position 5 is blue, which is the color of the sky.
(b) (i) A solution of potassium permanganate is violet. So position 7, corresponds to the color of potassium permanganate solution.
(ii) Danger or stop signal lights are red in colour. So position 1 corresponds to this colour.
