Name the element of group 13 which forms only covalent compounds.
Which element of group 13 forms amphoteric hydroxide?
Both Aluminium and Gallium forms amphoteric hydroxides.
What are silicates? Discuss briefly their structures.
Silicate is the general name given to a group of minerals which have silicon - oxygen bonds. Rocks, soils and clays consist of almost entirely silicate minerals such as quartz, mica, asbestos, feldspars and zeolites.
(i) Quartz is a crystalline form of silica (SiO2).
(ii) Mica is a potassium aluminium silicate KAl3Si3O10(OH)2.
(iii) Feldspar is a potassium silicate KAlSi3O8.
(iv) Asbestos is a calcium magnesium silicate CaMgSi2O6.
Structure: All silicates involve silicon-oxygen single bonds. These may either Si - O bonds or Si - O - bonds. The basic structural unit of all silicates is the 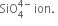 In this ion, silicon is sp3 hybridised. Each sp3 hybridised orbital of silicon combines with an orbital of the oxygen atom to form silicate ion which is tetrahedral in structure.
In this ion, silicon is sp3 hybridised. Each sp3 hybridised orbital of silicon combines with an orbital of the oxygen atom to form silicate ion which is tetrahedral in structure. 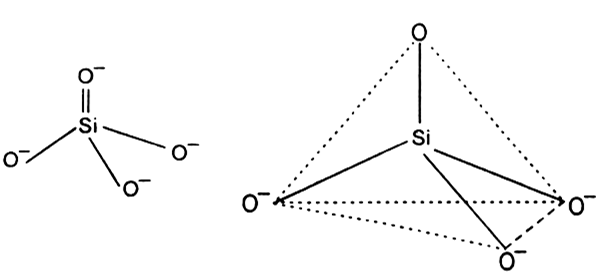
Such tetrahedral units  are linked together in different ways to give chains, rings, sheets and three-dimensional networks.
are linked together in different ways to give chains, rings, sheets and three-dimensional networks.
What are zeolites? What are the applications of zeolites?
 where n is the valence of cation? They may be considered as an open structure of silica in which a fraction n/x+y of the tetrahedral sites has been substituted by aluminium and void spaces are occupied by water molecules.
where n is the valence of cation? They may be considered as an open structure of silica in which a fraction n/x+y of the tetrahedral sites has been substituted by aluminium and void spaces are occupied by water molecules.Applications of zeolites. Zeolites are used:
(i) for softening of hard water
(ii) as desiccant
(iii) as a shape selective catalyst, e.g. ZSM-5 (zeolite sieve of molecular porosity 5) in converting methyl alcohol into gasoline (petrol),
(iv) as a catalyst in petrochemical industries
(v) as a detergent builder.
