CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Corrosion is slow and steady chemical reaction. When the surface of iron or metal is in contact with moisture and other gases in the atmosphere an electrochemical reaction occurs.
After some time, a layer of hydrated oxide is formed which weakens the metal and hence metal is said to corrode.
For example: Rusting of iron, black coating on silver and green coating on copper are examples of corrosion.
A chemical reaction of iron corrosion is shown below.
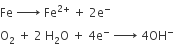
The Fe2+ ions are oxidised to Fe3+ ions.
The Fe3+ ions combine with OH- ions to form Fe(OH)3. This becomes rust (Fe2O3.xH2O) which is a hydrated ferric oxide.
Corrosion of metals is prevented by not allowing them to come in contact with moisture, CO2 and O2. This is achieved by the following method:
Corrosion is slow and steady chemical reaction. When the surface of iron or metal is in contact with moisture and other gases in the atmosphere an electrochemical reaction occurs.
After some time, a layer of hydrated oxide is formed which weakens the metal and hence metal is said to corrode.
For example: Rusting of iron, black coating on silver and green coating on copper are examples of corrosion.
A chemical reaction of iron corrosion is shown below.
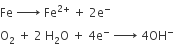
The Fe2+ ions are oxidised to Fe3+ ions.
The Fe3+ ions combine with OH- ions to form Fe(OH)3. This becomes rust (Fe2O3.xH2O) which is a hydrated ferric oxide.
Corrosion of metals is prevented by not allowing them to come in contact with moisture, CO2 and O2. This is achieved by the following method:
Redox reaction is the most important reaction in everyday life. It can be slow or fast. For example, combustion is an example of a fast redox reaction. One can easily notice heat and light.
On other hand, corrosion is slow redox reaction that occurs so slowly that noticeable heat and light are not produced.
Rancidity: The oxidation of fats and oils products when exposed to air, they become rancid and their smell and taste change.This is known as rancidity. It leads to bad smell and bad taste of food.
Methods to Prevent Rancidity