CBSE
Class 10 Class 12
Combination Reaction: The reaction in which two or more reactant combine to form a single product. For example,
Exothermic Reactions: Reaction in which heat is released along with the formation of products is known as an exothermic reaction.
For example,
Combination Reaction: The reaction in which two or more reactant combine to form a single product. For example,
Exothermic Reactions: Reaction in which heat is released along with the formation of products is known as an exothermic reaction.
For example,
Decomposition Reaction: The reaction in which a compound splits into two or more simple substances is called decomposition reaction.
A → B + C
Thermal decomposition: When decomposition is carried out by heating.
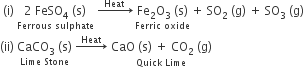
Electrolytic Decomposition: When decomposition is carried out by passing electricity.

Photolytic Decomposition: When decomposition is carried out in presence of sunlight.

Above reaction is used in black & white photography.
Endothermic Reactions: The reactions which require energy in the form of heat, light or electricity to break reactants are called endothermic reactions. For example,

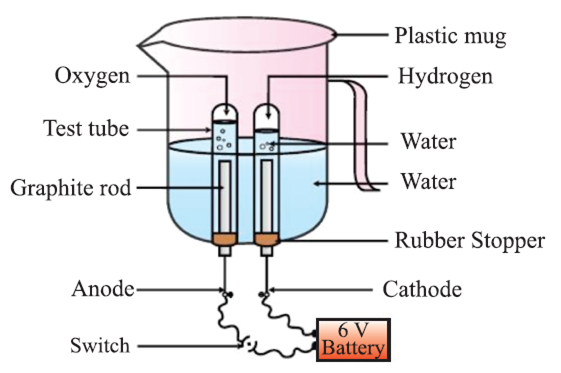
Displacement Reaction: The chemical reaction in which more reactive element displaces less reactive element from its salt solution.
Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → FeSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
The iron nail becomes brownish in colour by deposition of Cu and blues the colour of CuSO4 changes dirty green colour due to the formation of FeSO4.
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Zn is more reactive than copper.
Double displacement reaction: A reaction in which new compounds are formed by the mutual exchange of ions between two compounds.

A white precipitate of BaSO4 is formed, so it is also called precipitation reaction.
Oxidation:
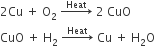
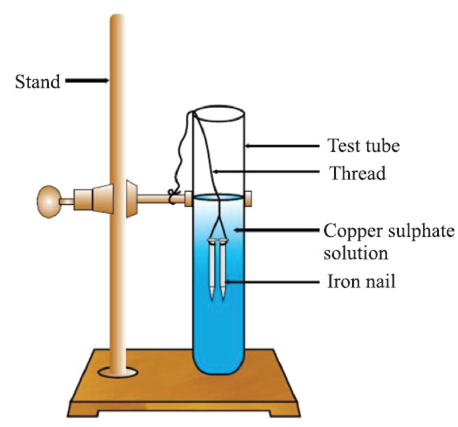
Element or compounds in which oxygen is added or hydrogen is removed are called to be oxidized.
Oxidizing agent: Compounds which can add oxygen or remove hydrogen element are known as oxidizing agents.
For example, when iron reacts with air, it forms iron oxide (rust)
4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3
Here, oxygen is added to iron, thus, iron is oxidized. Here oxygen is an oxidizing agent.
When cupric oxide reacts with hydrogen, it gives copper and water.
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
Here oxygen is removed from copper and oxygen is added to hydrogen. So, cupric oxide is reduced to copper and hydrogen is oxidized to water. Cupric oxide is oxidizing agent and hydrogen is reducing agent.
Reduction :
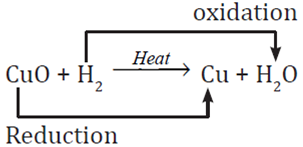
In this reaction CuO is reduced to Cu and H2 is oxidized to H2O. So, "oxidation and reduction taking place together is redox reaction".
Chemical reactions can be classified into following types: